What is PCT in sepsis? Can you test for sepsis? While the of the procalcitonin test should be interpreted by a doctor or qualified health provider, the are broadly classified as follows: Normal: to 0. L) Low risk of sepsis: less than 0. L Possible sepsis: between 0. Procalcitonin (PCT) – the biomarker of choice to aid in the diagnosis of sepsis.

PCT is synthesized primarily by the C-cells of the thyroid glan and to a lesser extent in the neuroendocrine tissue of other organs such as the lungs and intestines. A procalcitonin test measures the level of procalcitonin in your blood. A high level could be a sign of a serious bacterial infection, such as sepsis. The level of procalcitonin in the blood can increase significantly in systemic bacterial infections and sepsis. This test measures the level of procalcitonin in the blood.
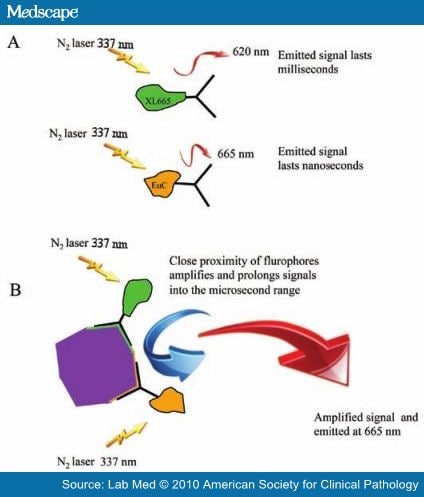
Among all sepsis markers, only PCT has achieved universal use throughout developed countries in the last decade. One major advantage of PCT compared with other biomarkers is its early and rapid increase in response to bacterial infections and sepsis. A key advantage is its relatively rapid rise in consonance with sepsis symptoms, Burnham offered.
Plasma PCT rises within about 3–hours of the initial clinical manifestations of sepsis and falls when severe infection resolves. Blood test show healthcare providers many things about your body, from the possibility of an infection to how well your body’s organs are working. These are some of the more common blood tests that may be done when a patient presents with possible signs and symptoms of sepsis. None of these tests can diagnose sepsis, but when the test are combined with information about your illness and a physical examination, they can help your doctor determine if you have sepsis:Complete blo.
See full list on sepsis. Urinalysis: Like the CBC, this simple urine test can tell your doctor a lot about your health, including if you have a urinary tract infection (UTI) or problems with your kidneys, such as a kidney stones. There is no special preparation to provide a urine sample for a urinalysis. Urine culture: A urine culture is performed to determine what bacteria or fungi has caused a UTI.
Urine for a culture must be obtained midstream. You will be given a special cleanser to wipe your genitals before you s. In addition to blood and urine tests, your doctor may want you to undergo other tests to identify where the infection may be. A pulse oximeter measures the oxygen saturation level of your blood. A chest x-ray can’t tell your doctor what type of infection you have. This tells your doctor how well your lungs are taking oxygen from the air and putting.
Physicians use PCT to distinguish bacterial sepsis from other causes of similar symptoms. An early and accurate diagnosis can save precious time, expense, and most importantly, lives. The point of care test is available in cassette format and is a way to assess sepsis in women around the time of childbirth.
Thus, in septic conditions in creased PCT levels can be observed 3-hours after infectious challenge.

Access PCT Assay Advancing patient care for sepsis while optimizing laboratory workflows The Access PCT assay is a procalcitonin blood test for laboratories supporting critical care settings. Access PCT offers state-of-the-art precision and low-end sensitivity for procalcitonin you can trust. PCT is the most accurate biomarker for the diagnosis of sepsis. In order to detect sepsis before it becomes life-threatening, a sensitive and rapid diagnostic test that can test for an accurate biomarker is required. Sensitivity and specificity of PCT for the diagnosis of sepsis has varied based upon population and underlying diseases.
After successful treatment intervention the procalcitonin value decreases, indicating a positive prognosis. Sepsis: PCT levels of 2. ProCT levels below 0. Reported sensitivity and specificity for the diagnosis of sepsis range from to 1, depending on underlying and coexisting diseases and the patient populations studied.