What is the history of ultrasound? Within a few years the group was recognised as one of the leading ultrasound research groups in the world. Jacques and Pierre Currie were the first to discover piezoelectricity.
This discovery was very important to ultrasound since the ultrasound transducers or probes receive and emit sound waves by using the piezoelectric effect. The Octason mark images allow us to see detailed fetal anatomy, and marks an important time in the development of ultrasound.

Obstetrician Ian Donald and engineer Tom Brown developed the first prototype systems based on an. Bionic ears are better known as hearing aids or cochlear implants. It amplifies sound for patients that are hard of hearing.
It’s a machine that enables expecting parents to view their unborn child via a screen. Graeme decided to work on creating hearing loss technologies because of hearing issues faced by his father and his invented Cochlear Implant technology continues to change the lives of many deaf and partially people around the world! This study marked the first ultrasound image of a fetal head.
Australia, but around the world’. Though ultrasound technology was already being used around the worl it was discovered that.
Sorry, it’s just the circle of life. From then onwards, the Ultrasonics Research Section of the Commonwealth Acoustics Laboratories Branch discovered a way to differentiate ultrasound echoes bouncing off soft tissue in the body and converting them to TV images. Subsequent advances in the field took place concurrently in several countries. High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) is a non-invasive therapeutic technique that uses non-ionizing ultrasonic waves to heat tissue. HIFU can be used to increase the flow of blood or lymph, or to destroy tissue, such as tumors, through a number of mechanisms.
Enjoy, it is more educational in a fun way. List: HOUSEHOLD ITEMS. Owen gun, a simple submachine gun effective in wet conditions, invented by Evelyn Owen. Most of the implantable monitors invented so far rely on high tech and expensive detectors such as CT scans or MRI.
Corresponding Author. Aeroguard insect repellent. The ultrasound scanner was designed and built in Glasgow. It was a collaboration between a number of Scottish pioneers and began with the work of Professor Ian Donal Dr John McVicar and Tom Brown. Medical ultrasound (also known as diagnostic sonography or ultrasonography) is a diagnostic imaging technique, or therapeutic application of ultrasound.
This website has been archived and is no longer updated. The content featured is no longer current and is being made available to the general public for research and historical information purposes only. The technology—published today in the journal ACS Sensors— has been granted an international provisional patent.

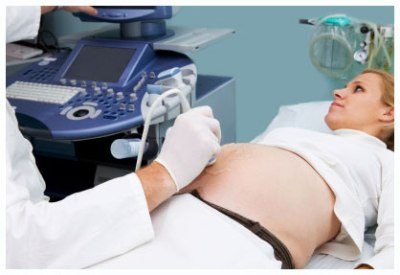
Ultrasound is a scan used to study internal body structures. Speak to your doctor or specialist about whether an ultrasound is required. How is an ultrasound scan performed? While studying ultrasound technology, CSIRO’s Ultrasonic Research Centre discovered a way to differentiate ultrasound echoes bouncing off soft tissue in the body and converting them to TV images. An ultrasound scan is performed using a hand-held scanner, or transducer, connected to a computer.
Saline infusion sonohysterography (SIS) or saline ultrasound uterine scan uses a small amount of saline (salt solution) inserted into the uterus (or womb) that allows the lining of the uterus (endometrium) to be clearly seen on an ultrasound scan. Today, the technology has. Clark’s invention was inspired by his father’s poor hearing. In the beginning, Doppler ultrasound was also strictly an analysis of audible sound.
It was discovered by scientists at the Commonwealth Acoustic Laboratories’ Ultrasonic Research Centre, who were studying ultrasound technology in an effort to convert ultrasound echoes into TV images. To reveal where an object is and what shape it is the sound bounces off the object. And by creating this medical tool it has become an inceradicably useful to many doctors, nurses and midwives.
Researchers at the Commonwealth Acoustic Laboratories in Sydney developed the technology – which uses high pitched sound to ‘see’ inside the human body – after becoming concerned about the effects of X-rays on pregnant women.