Can You Transfer Assets Out Of An Irrevocable Trust ? How do you transfer title to trust assets? Can trustee distribute assets to beneficiaries? Is there a tax obligation for a trust beneficiary?
Can I transfer property to beneficiary?
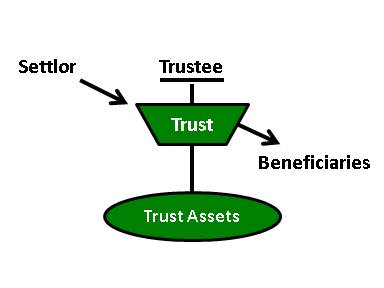
The grantor essentially transfers all the ownership of the associated assets into the trust and removes the right of ownership of those assets to the trust itself. When a Trust consists solely of cash, then the distribution is easy. The Trustee can write a few checks, make the Trust distribution, and end the Trust administration. A practice note about how to transfer trust assets to or from a trust and between trustees, with details of how to transfer the most common types of trust asset. An asset’s tax basis is its value for income tax purposes.
When an asset is sol the fair market value of the asset is assessed against the tax basis of the asset (basically, how much did you buy it for and how much did you sell it for?). If the fair market value is greater than the tax basis, then you will have a taxable capital gain.
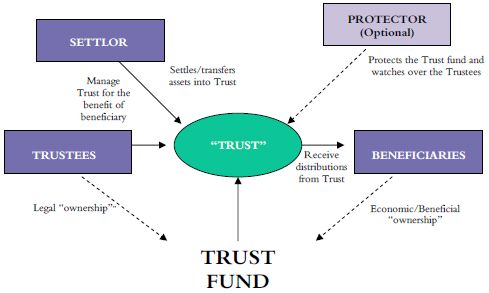
Note that the beneficiary wil. See full list on jacksonwhitelaw. Now, onto the basics of trusts.
Revocable trusts are created during the grantor’s lifetime (the grantor being the original owner of the assets), making it a living trust. The grantor usually serves as the trustee and the beneficiary during their lifetime, and upon their death a successor trustee and successor beneficiary will take over management and distribution of trust assets (respectively). With a revocable trust, the terms of the trust can be amended at any time by the grantor, and the t. The key distinction with distributions from an irrevocable trust will be whether or not it is considered a grantor trust. If the irrevocable trust uses the grantor’s social security number, it qualifies as a grantor trust, and the trust’s income is recognized on the grantor’s individual tax returns each year.
Grantor trusts do not get a step-up when the grantor dies. The asset’s adjusted tax basis is based on the values reported on the grantor’s tax returns, and carries over to the beneficiar. The difference in taxation of long term capital gains vs.
Whether the trust is revocable or irrevocable, the holding period recognized by the trust carries over to the beneficiary—it does not restart when the assets are distributed. That means that a stock that was purchased months ago by the trust will carry over the 6-month holding period t. The US tax code allows entities to utilize pass-through taxation in certain situations. In this case, pass-through taxation instructions would need to be clearly defined in the trust agreement.

If so, then the trustee will provide the beneficiary with a Schedule K-each year. The beneficiary would then report the income (or loss) from the trust in their annual tax return. Property that is specifically bequeathed by will is not considered income for the beneficiary. There is no gain or loss recognized as a result of the transfer , though the beneficiary will inherit a carryover tax basis. Typically, the trustee will inform the beneficiary of the tax basis and applicable holding period requirements.
If a single person is listed as the beneficiary of the contents of the trust, for example, the successor trustee simply transfers ownership of all assets to the sole beneficiary. Where the trust identifies all assets and designates direct transfer to specific beneficiaries, this also makes for easy distribution. Go online and obtain a tax identification number from the Internal Revenue Service for the trust.
Open a bank account in the name of the trust. Close out any bank accounts the grantor established for the trust and put the proceeds into the new trust bank account. Cash in any life insurance policies that name the trust as beneficiary and put the proceeds into the trust bank account.
If the grantor owned securities not specifically given to a beneficiary, have the grantor’s broker sell the securities as soon as possible. When you receive the proceeds check, deposit it into the trust’s bank account. Check if any real estate the grantor owned was given to a specific beneficiary. Either draft or have an attorney draft a Trustee’s Deed transferring ownership of the real estate out of the trust to the beneficiary.
After it is signe you and the beneficiary must go to the clerk of the court to have the deed recorded in the public records. If the real estate is not left to a named beneficiary, contact a local real estate agent and have the real estate sold. Be sure the real estate is sold at the fair market value. Place the sale proceeds in the trust bank account. Distribute the assets after they have been liquidated according to the terms of the trust.
For example, if the trust bank account has $600and the amount is equally divided among three beneficiaries, each beneficiary should receive one-third of the assets, which would be $20000. Be sure each beneficiary signs a receipt acknowledging she received the full amount to which she was entitled. When you close out the grantor’s accounts, be sure any checks are made payable to the trustee in the name of the trust, for example, “John H. Doe, Trustee of the Jane A. Doe Revocable Trust Dated Jan.
You will have to file a trust income tax return, so keep careful records of the value and disposition of each asset owned by the trust. While a revocable trust avoids probate, it does not avoid estate taxes, so if estate taxes are due and an estate tax return is also necessary. Some financial institutions also call this a POD designation (or “Pay on Death”). There are many ways to avoid probate, the trick is finding the best solution for you.
Instant Downloa Mail Paper Copy or Hard Copy Delivery, Start and Order Now! Real Estate, Family Law, Estate Planning, Business Forms and Power of Attorney Forms. To distribute a particular asset to a particular beneficiary , read the trust document to determine which beneficiary needs to get which asset.
To execute a trust , its property must be transferred to the trustee. The other possibility is that the trust property can be transferred to a beneficiary after the trust is created. Trusts are subject to state law, so you want to check the law of the state where the trust is located to ensure that you are following the right procedure.
In exercise of their dispositive powers, trustees transfer income and capital to beneficiaries. For commentary on the different types of payments, see the Payments to trust beneficiaries guidance note. Most often, particularly in the case of income distributions, the payments will be in cash. For items of high value, a very detailed description of the asset should be included. Even if your intent is to place all of your assets in the trust , a pour-over will is a way of ensuring no asset is forgotten.
The Transfer of Assets to Beneficiaries Including Real and Personal Property and Satisfying Tax Lien Waivers Many folks want to leave a financial legacy to their spouse, children, grandchildren and others. If a trust transfers an asset to a beneficiary for no consideration, the trust is treated as disposing of the asset for its market value for capital gains tax purposes. One of the largest assets most people own is their home and this is likely an asset you want to transfer into your trust.
You can transfer your home (or any real property) to the trust with a dee a document that transfers ownership to the trust.