What do you do with a testamentary trust upon? When is a testamentary trust the best option? What is a testamentary trust and do I need one? How do I set up a testamentary trust?

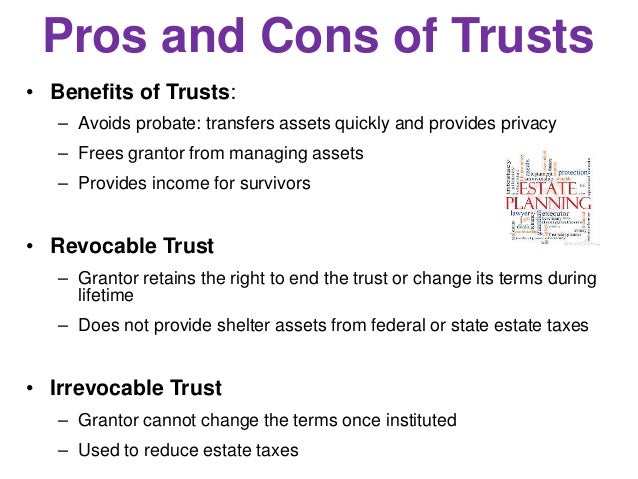
Living trusts can be revocable, meaning you can cancel the trust and take your property back, or irrevocable, but both allow you to put property into the trust while you are alive. If the trust endures for many years, the court fees can eat up a significant chunk of money. But the protections aren’t free. Usually this type of trust is made within a will often to create a trust for minors.
When a trust is included in a will, the will goes into effect immediately, but the trust is not actually created until after the death of the will maker. The expense explains, in. See full list on nolo. Non- testamentary trusts take effect when the grantor signs the trust , has it notarize and transfers property into the trust.

This type of trust is called an inter vivos or living trust because it goes into effect during the grantors lifetime. Inter vivos trusts can be either revocable or irrevocable. In contrast to these types of trusts, a testamentary trust does not take effect until death of the trust maker, and at that time the trust becomes irrevocable.
Because it does not take effect during the grantors lifetime, the grantor is free to make changes to the trust until his or her death. Testamentary trusts are most often used to leave money to children through a will. Using testamentary trust in a will allows you to leave a gift to a child and also to name a trusted guardian as trustee of that gift.
Unlike living trusts, testamentary trusts do not avoid probate. It is frequently used when the beneficiary or beneficiaries are children or disabled people. A testamentary trust created through a will must go through probate before the trust is created.
In this Court, it is administered as a separate case file. Probate is necessary to move that property into the name of the trust , just as it would be to transfer it into the names of living beneficiaries. Overall, however, there are two categories: living and testamentary. A will can be used to create a. To create a testamentary trust in a will, the settlor must designate a trustee and specify the beneficiaries.
One key purpose of a living trust is to allow assets within the trust to avoid the legal proceedings. As mentioned above, a testamentary trust comes into effect not until the settlor dies. Interested parties, which are relatives, friends and creditors of the deceased have the legal right to challenge a will and the testamentary trust during probate.
A trust can also be created after someone’s death, called a testamentary trust. If the trust becomes effective after the death of the settlor, the trust is called a testamentary trust. A trust , by definition, is an arrangement where property or assets are managed by one person for the benefit of another person. A revocable living trust skips this legal process, through which assets are distribute since the assets are already held by the trust.

However, with a testamentary trust , the assets haven’t been transferred and are still owned by the settlor until he or she dies. Beyond the advantage of costing less than a living trust a testamentary trust is advantageous if you want your estate to go through probate. However, the vast majority of folks that get a revocable living trust end up having to deal with probate , just like the folks that get a testamentary trust , because they didn’t use or fund the trust appropriately.
Unlike trusts created during the lifetime of the Grantor, a testamentary trust does not become effective until the Grantor has died and his Will has been through probate. It is different from a living trust , which can be created and go into effect during your lifetime. Example: A parent specifies in her will that upon her death her assets should be transferred to a trustee or co-trustee. INSTRUCTIONS FOR ESTABLISHING A TESTAMENTARY TRUST These instructions are intended as a guideline only and should not be relied upon as a comprehensive list of duties in a testamentary trust. A fee is required at the time of filing.
Current Court Costs are.