Australia Income Tax Treaty exempts superannuation from U. We can provide a Tax Opinion to secure the legal exemption. The bare trust is merely the registered holder of the property until the loan is repaid. If and when the loan is repaid the legal ownership of the investment property will revert to the trustee of the SMSF.
All property related costs can be paid by the SMSF.
A Bare Trust is set up only if you need to take out a loan (from a bank, a private lender, or any other source). When you’ve identified the property and supplied us with the relevant details, we can set up your bare trust in a matter of hours. Can a bare trustee be a trustee of a trust?
The Bare Trust isolates the property acquired through borrowing from other assets held in the SMSF. Having an Individual Trustee behind the Bare Trust may not be a prudent strategy as an Individual Trustee can die, whereas a Corporate Trustee does not die because a company. Again, this can be organised with your accountant.
Once the declaration has been signed and date your relevant state registry office will need to verify and stamp the trust deed.

There is a view that the bare trustee structure causes an in-house asset issue. Therefore, this bare trust can be seen as a related trust , and an investment in a related trust is seen as an in-house asset. You can apply for self-managed super funds specific advice (SMSFSA) about: 1. SMSF : Avoid bare trust mistakes. See full list on ato. Subject to limited exceptions allowed under SISA, trustees of SMSFs are prohibited from borrowing money.
The rules are in section 67A and section 67B of the SISA. Section 67A of the SISA 2. Those arrangements must meet the conditions set out in former subsection 67(4A) of the SISA. Super law requirements for LRBA by super trustees 2. Changes to other laws relating to LRBAs 3. Asset being acquired and replacement assets 5. Special in-house asset rules 6. A Bare Trust Deed is established to allow a Superannuation Trust Deed to borrow money for purchasing assets like real estate, listed securities, units in a Unit Trust Deed and even works of art.
A bare trust exists when there is only one trustee, one legally competent beneficiary, no specified obligations and the beneficiary has complete control of the trustee (or “nominee”).

Typically theses are set up using bare trusts and while that may be a preferred way to do so, there are some basic mistakes that can lead to consequences. A common example of a bare trust is used within a self-managed fund to hold assets under a limited recourse borrowing arrangement. A key advantage of the bare trust is that it is not a reportable entity and does not require an ABN or TFN. A Bare Trust is a trust where the beneficiaries are absolutely entitled as against the trustee and one in which the trustee has no active duties to perform.
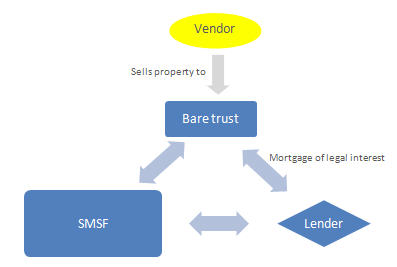
Variously called a Custodian Trust , Bare Trust or other terms the purpose of this structure is to act as a separate entity to hold the assets which are purchased and likely subject to security for the loan. Though the Custodian Trust holds the property, or other asset, the loan is made to the SMSF. At that time, the bare trust was establishe with a trustee incorporated for that purpose. Once the loan is repai the property will move from the Bare Trust into the SMSF. The diagram below sets out the most common structure.
As you can see from the diagram below, the property is held by the Holding Trust while the loan is taken out by the SMSF. The property must be purchased and held in the name of the trustee of the bare trust. You would have to prove to the court that your bare trust owned the property on behalf of your SMSF. The asset could be frozen in the meantime. This can be time consuming.
You will need a separate bare trust for each property, however you can use the same trustee company each time if you own multiple properties. Another potential problem with bare trusts was highlighted by the recent BC Court of Appeal decision in Graham v.