
A legal entity , typically a business , that is defined as detached from another business or individual with respect to accountability. A separate legal entity may be set up in the case of a corporation or a limited liability company, to separate the actions of the entity from those of the individual or other company. These use the suffix “CIC”.
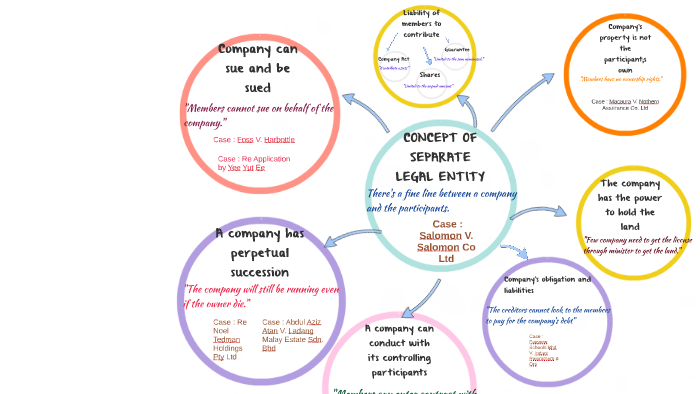
Is a partnership a separate legal entity ? Difference between Sole Proprietors and Companies. In this example, we use a company as a separate legal entity. Separate legal entity means any entity created by interlocal agreement the membership of which is limited to two or more special districts, municipalities, or counties of the state, but which entity is legally separate and apart from any of its member governments. This is confirmed in the House of law in the case of Salomon vs. Limited liability also states that shareholders are not personally liable for their company’s debts.
See full list on lawaspect. This principle enables each company in a corporate group to be treated as a separate legal entity distinct from other companies within the group. This has significant implications in tort cases, wherein tort creditors of a company in a group could only enforce their legal right against the debtor company. To this extent, shareholders of the debtor company are not liable for the company’s debts beyond their initial capital investment.

Therefore, the principle of separate legal entity has an adverse impact especially on tort creditors who bear an involuntary and uncompensated risk. As the corporate group could move the assets between companies in the group, it allows the “group” to escape its liability from claimants, to the fact that creditors may look only the assets of the debtor company itself. It implies that shareholders are not personally liable for their company’s debts.
According to s51 shareholders do not have to contribute more than what they have invested. Yet, the privileges of limited liability do not necessarily flow from the principle of separate legal entity. While all corporations enjoy the benefits of separate legal entity , an unlimited liability company does not enjoy the privilege of limited liability. As a result, the company liability is only limited so that creditors may only take action against the company’s assets rather the personal assets of its members.
Based upon principle of economic efficiency, four reasons justify the doctrine of limited liability. Firstly, the limited liability decreases the need for shareholders to monitor the managers of companies they invested in, in order to facilitate the separation of ownership and control in large corporations. Yet, the corporate group structure typically involves one corporate investor who controls the decision-making process of its subsidiaries. If the principle of limited liability is voi shareholders could loss their entire wealth by reason of the failure of one company in which they hold equity on.
However, this argument is diminished if there is a single parent company shareholder that has no market for shares in subsidiary. Thirdly, limited liability promotes market efficiency, as the price at which shares are traded does not depend upon the wealth of each sh. At the same time, courts have acknowledged that the corporate veil of a company may be pierced to deny shareholders the protection that the principle of separate legal entity normally provides. It is noted that there are exceptions under the common law and statutory to lift the veil in relation to torts committed by a group company.

In the context that a subsidiary acts as an agent, the mere exercise of control over the subsidiary by a parent company will serve as an insufficient ground. In this article, legal establishment of a corporate body within the context of separate legal entity have been evaluated. Each concept has its impact on tort creditors and stakeholders.
However, in certain situations, it becomes necessary to “pierce the corporate veil” and deal with each entity within the context of binding laws. What is meant by separate legal entity? What do you mean by separate legal entity concept? How to establish a separate entity? In terms of day-to-day business, a separate entity runs separately from the owner, with a separate bank account and transactions, buying and selling products or services or both, and receiving and paying out its own money.
This means that most of the legal entity in business is separate from another business or individual with value to accountability. This case has formed the basis of company law and corporate theory. If it was, the business belonged to it and not to Mr. Corporate theory has certain principles which practitioners and academics have struggled to define.
Ltd which has formed the basis of company law globally is one such example. In this paper we explore on the following statement made by Lord Halsbury L. Salomon’s case and analyze the courts’ approach to the separate entity principle. Either the limited company was a legal entity or it was not. Since the company was in need of more funds, they sought £0from Broderip.
Salomon’s debenture was then assigned. Much of the criticism has been based on the fact that corporate veil may at times lead to injustice. The case of Salomon V. Criticism is also mounted against Salomon’s case on the basis that priority is given to the separate identity principle over the economic reality of a one-person company.
Kahn-Freund further called for the abolition of private companies. First, the unanimous ruling made by the House of Lords in this case gives incorporators the benefit of limited liability even in situations where it may be deemed unnecessary. In this context, ‘piercing of corporate veil’ describes situations wherein the separate entity principle may be deemed unfair and the courts may make decisions contrary to this principle on various grounds.
This is an area which is said to be ill-define inconsistent and quite unpredictable. In other words, there are certain situations in which the courts can legitimately disregard the separate legal entity principle. In this context, statutory exceptions include provisions that penalize office holders by imposing personal liability. Several statutory provisions have introduced exceptions to the separate legal entity principle.
In pursuant to the ‘fraudulent trading’ provision, if it appears that fraud has been used in carrying out business transactions, the court may on application of the liquidator declare any of the parties to the business liable for making contributions as may be deeme. There is no doubt that the decision in Salomon’s case established the separate legal personality of a company, allowing shareholders to carry on trading with minimal exposure to the risk of personal insolvency in the event of a collapse. It remains, however, a daunting task for academics and practitioners to find a basis in which the courts may be justified to lift the corporate veil. This is largely due to the fact that this is an area where case facts and personal views of judges have a bearing on the outcome.
Nonetheless, the principle in Salomon case is widely recognized and followed in courts. Bourne on Company Law. Salomon’s case has become a landmark company case law in the UK and is often cited in most cases within the area of compa.
Some reflections on Company Law Reform. Corporate world today: courts respond to limited liability and board’s decision making – a fight for a justice or rather prosperity at stake? Corporations and associations law: principles and issues. Business law, 9th edition.
Harlow, Pearson Longman. Piercing the corporate veil” – the never ending story? Commercial and business organizations law in Papua New Guinea. A two-edged sword: Salomon and the separate legal entity doctrine.
Routledge-Cavendish Puig, G. THE ADVANTAGES OF INCORPORATION. This evolution was gradual and involved subtle changes that occurred on a number of fronts. There are many factors that influence incorporation. In the United States, a separate legal entity or SLE refers to a type of legal entity with separate accountability.
A Company is a Separate Legal Entity. One of the most distinctive features of a Company, as compared to other organizations, is that it acquires a unique character of being a separate legal entity. Hence, when you register a company, you give it a legal personality with similar rights and powers as a human being. Under the concept of separate legal entity , a company will becomes a body corporate that exists separately with its owner and distinct from its individual members and directors.
In others wor the corporation is an entity just like human being created using legal and official purpose. Separate entity is basically an accounting concept where as separate legal entity is a legal concept which overrules the accounting concept of separate entity. Parent companies can benefit from owning subsidiaries because it can enable them to acquire and control.