What does public limited liability company mean? What are some examples of limited companies? It is compulsory to call a statutory general meeting of members, in the case of a public company, whereas there is no such compulsion in the case of a private company.
A company at its crux, is an artificial person created by law. Its an association of individuals having a separate legal existence, perpetual succession and a common seal.
Its capital is generally divided into transferable shares, subject to certain conditions. See full list on evoma. Both private and public limited companies have its own advantages and disadvantages. A private limited company is a business entity that is held by private owners. This type of entity limits the owners liability to their ownership stake, and restricts shareholders from publicly trading shares.
They are freely transferred among the members and the people trading on stock markets. By law, a public company has a responsibility to its shareholders to maximize shareholder profits and disclose information about business operations. The company and its management can be sued for self-dealing, making material misrepresentations to shareholders or hiding information that federal securities laws require to be disclosed.

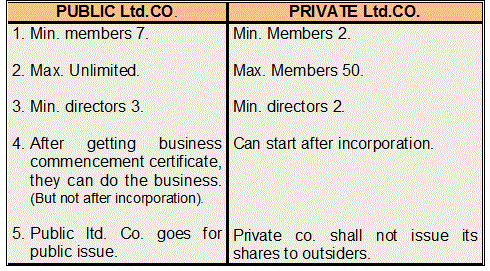
Members: In order for a company to be public , it should have a minimum of members (maximum unlimited). Perpetual succession: As per company law, perpetual succession means that the company continues its existence even any owner or member dies, goes bankruptcy, exits from the business and transfers his shares to another person. Prospectus: Prospectus is a detailed statement that must be issued by a company that goes public. However, private limited companies do not need to issue a prospectus because the public is not invited to subscribe for the shares of the company. In order to be eligible to run as a public company , it should obtain another document called a trading certificate.
A public company is not authorised to begin its business operations just upon the grant of the certificate of incorporation. Limited liability: The liability of a public company is limited. No shareholder is individually liable for the payment. The public limited company is a separate legal entity, and each shareholder is a part of it.
It should have a minimum of and can have a maximum of board of directors. They are elected from among the shareholders by the shareholders of the company in annual general meetings. The elected directors act as representatives of the shareholders in managing the company and taking decisions. Having a bigger board of directors therefore benefits all shareholders in terms of transparency as well as fostering a democratic management process. Expensive: Going public is an expensive and time consuming process.
A public company must put its affairs in order and prepare reports and disclosures that match with SEBI regulations concerning initial public offerings (IPO). The owner has to hire specialists like accountants and underwriters to take the company through the process. Loss of Management Control: Once a private company goes public , managing the business becomes more complicated.

The owner of the company can no longer make decisions independently. Even as a majority shareholder, they are accountable to minority shareholders about how the company is managed. Also, company owners will no longer have total control over the composition of the board of directors since SEBI regulations place restrictions on board composition to ensure the independence of the board from insider impact.
Increased Regulatory Oversight: Going public brings a private company under the supervision of the SEBI and other regulatory authorities that regulate public companies, as well as the stock exchange that has agreed to list the companys stock. This increase in regulatory oversight significantly influences management of the business. A public limited company is a company listed on a recognized stock exchange and the stocks are traded publicly. It is privately held by its members only. The minimum number of members required to start a public company is seven.
Definition: A public company can sell its own registered shares to the general public. A private company can sell its own, privately held shares to a few willing investors. A limited company is a public limited company that is owned by the general public. All the shares of a private limited company rest only in the hands of a few people or promoters. Pvt Ltd Company is owned by a group of promoters.
The company is not in the hands of a few promoters but the public owns it. This means that a number of people can jointly own the business. Private Limited Companies : Private limited companies , sometimes referred to as limited companies , are a form of Joint Stock Company.
The financial capital of the company is divided into shares. The main difference is that the shares of a public limited company can be transferred freely on the stock exchange to anyone, a private limited company cannot sell shares this way. The accounts must be made available for public viewing. This guide provides examples including comparable company analysis, discounted cash flow analysis, and the first Chicago method.
One can come across many differences between the two. The terminology itself shows that the two are different ‘“ one is public limited and the other is private limited. Controlling here means that they have enough shares to appoint directors and generally dictate the business development path the company. Exempt Private Company (EPC) is one which: Has a maximum of shareholders. No corporation is a shareholder.
May have more than shareholders. May raise capital by offering shares or debentures to the public. Incorporated and Limited are among a number of different types of business structures including sole traders, partnerships, limited liability companies , limited companies , incorporations, private limited companies , etc.
Public Company Limited by Shares.