How is PDA diagnosed? Which direction does blood flow through the ductus arteriosus? What is PDA in newborn?

However, a large patent ductus arteriosus left untreated can allow poorly o. See full list on mayoclinic. A small PDA might cause no signs or symptoms and go undetected for some time — even until adulthood. Patent ductus arteriosus symptoms vary with the size of the defect and whether the baby is full term or premature. A large PDA can cause signs of heart failure soon after birth. Genetic factors might play a role.
After birth, the ductus. Risk factors for having a patent ductus arteriosus include: 1. Family history and other genetic conditions. A family history of heart defects and other genetic conditions, such as Down syndrome, increase the risk of having a PDA. Rubella infection during pregnancy.
A small patent ductus arteriosus might not cause complications. Larger, untreated defects could cause: 1. High blood pressure in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). A large patent ductus arteriosus can lead to Eisenmenger syndrome, an irreversible type of pulmonary hypertension.
A patent ductus arteriosus c. Here are some of the basics: 1. Quitting smoking, reducing stress, stopping birth control — these are all things to talk to your doctor about before you get pregnant. Include a vitamin supplement that contains folic acid. The ductus arteriosus is a hole that allows the blood to skip the circulation to the lungs.
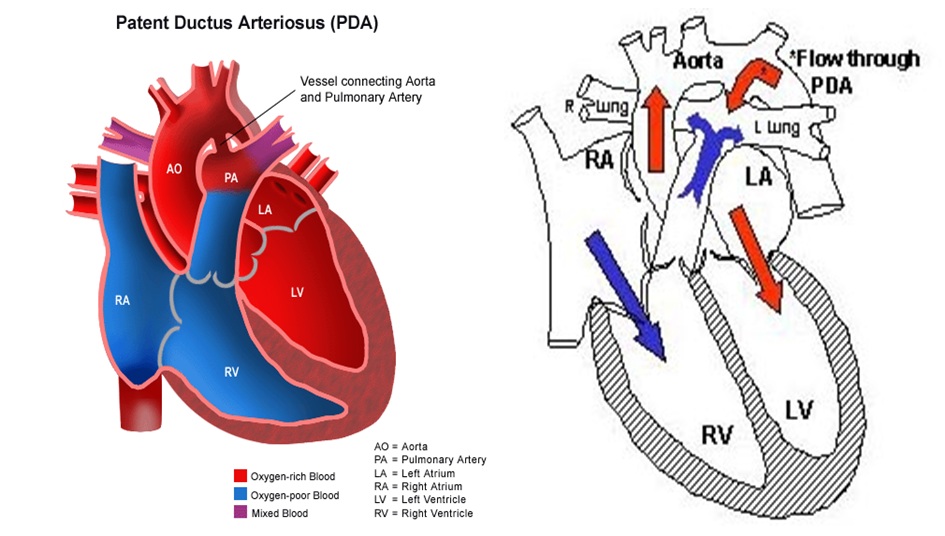
However, when the baby is born, the blood must receive oxygen in the lungs and this hole is supposed to close. If the ductus arteriosus is still open (or patent ) the blood may skip this necessary step of circulation. PDA produces a left to right shunt that leads to increased blood flow to the lungs. The amount of blood that flows through the ductus and the degree of symptoms is determined by the difference. Clinical manifestations of a PDA are determined by: 1. Degree of left to right shunt, which depends on the size and length of the PDA 2. The difference between pulmonary and systemic vascular resistance 2. The first heart sound is normal but the second heart sound is obscured by a continuous cre.
Chest x-rays and electrocardiograms may be helpful, but are less sensitive and specific than echocardiography. Heart Failure due to cardiac volume overload 1. Infants present with: failure to thrive (FTT), poor feeding, respiratory distress 2. Infective Endocarditis: vegetations accumulate at the pulmonary end of the PDA and shower the lungs with septic emboli 3. Pulmonary Hypertension 1. If a newborn has a PDA, pharmaceutical treatment is used to encourage closure, primarily with indomethacin or ibuprofen. If the newborn fails to respond to medical management, surgery or cardiac catheterization procedures are recommended.
Surgery is indicated for infants with heart failure who have failed to respond to medical management and for any c. Johns Hopkins University, Helen B. Hoffman JI, Kaplan S. The incidence of congenital heart disease. Reller M Strickland MJ, Riehle-Colarusso T, et al. Coggins KG, Latour A, Nguyen M. This is an example of patent ductus arteriosus heard at the pulmonic position. Before birth, the two major arteries—the aorta and the pulmonary artery—are connected by a blood vessel called the ductus arteriosus. Shortly after birth the patent ductus closes and turns into a ligament.
A heart murmur is an extra or unusual sound heard during the heartbeat. Heart murmurs also have other causes besides PDA , and most murmurs are harmless. It occurs when a temporary blood vessel, called the ductus arteriosus , doesnt close soon after birth. Symptoms may be minimal or severe. In rare cases, the defect can go undetected and can exist in adulthood.
Correction of the defect is usually successful and restores the heart to its normal function. In a normally functioning heart, the pulmonary artery carries blood to the lungs to collect oxygen. The oxygenated blood then travels through the aorta (the bodys main artery) to the rest of the body.
In the womb, a blood vessel called the ductus arteriosus connects the aorta and pulmonary artery. It allows blood to flow from the pulmonary artery to the aorta and out to the body without going through the lungs. This is because the developing child gets oxygenated blood from the mother, not from their own lungs. Soon after a baby is born, the ductus arteriosus should close up to prevent mixing oxygen-poor blood from the pulmonary artery with oxygen-rich blood from the aorta.

When this doesnt happen, the baby has patent ductus arteriosus (PDA). If a doctor never detects the defect, the baby may grow into an adult with PDA, although this is rare. Premature birth can put babies at risk. This means that symptoms may be very mild to severe.
PDA is more common in girls than boys. In the rare case that PDA goes undetecte an adult with the defect may experience symptoms that include heart palpitations , shortness of breath , and complications such as high blood pressure in the lungs , an enlarged heart , or congestive heart failure. A doctor will usually diagnose PDA after listening to your childs heart.
A chest X-ray may also be necessary to see the condition of a babys heart and lungs. An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create a picture of the babys heart. Its painless and allows the doctor to see the size of the heart. It also lets the doctor see if theres any abnormality in blood flow. Echocardiogram is the most common method to diagnose PDA.
An EKG records the electrical activity of the heart and detects irregular heart rhythms. In babies, this test can also identify an enlarged heart. In cases where the opening of the ductus arteriosus is very small, no treatment may be necessary.
In this case, your doctor will want to monitor the PDA as the baby grows. The opening can close as an infant gets older. In a premature baby, a drug called indomethacin can help close the opening in PDA. When given intravenously, this medication can help constrict muscles and close off the ductus arteriosus. This type of treatment is typically only effective in newborns.
In older infants and children, further treatment may be necessary. However, younger infants can have this treatment if they have symptoms. If the opening is large or it doesnt seal on its own, surgery may be necessary to correct the defect. For surgical procedures, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to prevent bacterial infection after leaving the hospital. In an infant or child with a small PDA, your doctor may recommend a trascatheter device closure procedure, according to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
This procedure is done as an outpatient and does not involve opening the childs chest. A catheter is a thin flexible tube that is guided through a blood vessel starting in the groin and is guided to your childs heart. A blocking device is passed through the catheter and placed in the PDA. The device blocks the blood flow through the vessel and allows normal blood flow to return. Its very unusual for PDA to go undetected into adulthood.
Most cases of PDA are diagnosed and treated soon after birth. The larger the opening is, the worse the complications. If it does, however, it can cause several health problems.
However rare, untreated adult PDA can lead to other medical conditions in adults, such as: In very serious cases of untreated adult PDA, extra blood flow can eventually increase the size of the heart, weakening the muscle and its ability to pump blood effectively. This can lead to congestive heart failure and death. Recovery for premature babies will depend on how early the baby was born and whether or not other illnesses are present.
Most infants will make a complete recovery without experiencing any PDA-related complications. The murmur , along with symptoms of heart failure in a premature infant, most often lead to the diagnosis of patent ductus arteriosus. In patients with PDA , the ductus arteriosus stays open ( patent ), and blood can flow from the aorta into the pulmonary artery. If it stays open, the result is a condition called patent ductus arteriosus ( PDA ). Ductus arteriosus is a normal connection or opening in a fetus between the descending thoracic aorta and the pulmonary artery. In normal development, the ductus arteriosus closes after birth.
Manifestations depend on the size of the PDA and the age of the chil but a continuous murmur is characteristic an if lou has a “machinery-sounding. LISTEN WITH HEADPHONES. Recording made with a Thinklabs One Digital Stethoscope. Continuous murmur in a 5-year-old who has a restrictive patent ductus arteri.
Certain breeds are predisposed and if the puppy with a heart murmur is from one of those breeds, the suspicion of a patent ductus arteriosus may be higher.