How is PDA diagnosed? When does a PDA close? Where can you best hear PDA murmur? What is PDA in medical term?
Patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is a congenital heart defect – a structural heart problem that is present at birth.
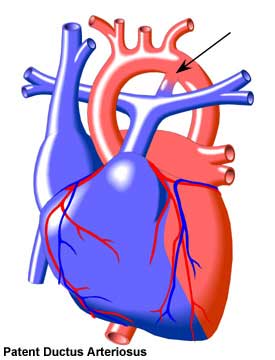
The pulmonary artery carries blood from the heart’s right lower chamber (ventricle) to the lungs, where it is loaded up with oxygen. However, a large patent ductus arteriosus left untreated can allow poorly o. See full list on mayoclinic. A small PDA might cause no signs or symptoms and go undetected for some time — even until adulthood.
Genetic factors might play a role. After birth, the ductus. Risk factors for having a patent ductus arteriosus include: 1.

Family history and other genetic conditions. A family history of heart defects and other genetic conditions, such as Down syndrome, increase the risk of having a PDA. Rubella infection during pregnancy. A small patent ductus arteriosus might not cause complications.
Larger, untreated defects could cause: 1. High blood pressure in the lungs (pulmonary hypertension). A large patent ductus arteriosus can lead to Eisenmenger syndrome, an irreversible type of pulmonary hypertension. A patent ductus arteriosus c. Here are some of the basics: 1. Quitting smoking, reducing stress, stopping birth control — these are all things to talk to your doctor about before you get pregnant. Include a vitamin supplement that contains folic acid.
An unclosed hole in the aorta. The ductus arteriosus is a hole that allows the blood to skip the circulation to the lungs. However, when the baby is born , the blood must receive oxygen in the lungs and this hole is supposed to close. If the ductus arteriosus is still open (or patent) the blood may skip this necessary step of circulation.
In normal circulation, the right side of the baby’s heart pumps blood through the pulmonary arteries to their lungs.

It occurs when a temporary blood vessel, called the ductus arteriosus , doesnt close soon after birth. Symptoms may be minimal or severe. In rare cases, the defect can go undetected and can exist in adulthood. Correction of the defect is usually successful and restores the heart to its normal function. In a normally functioning heart, the pulmonary artery carries blood to the lungs to collect oxygen.
The oxygenated blood then travels through the aorta (the bodys main artery) to the rest of the body. In the womb, a blood vessel called the ductus arteriosus connects the aorta and pulmonary artery. It allows blood to flow from the pulmonary artery to the aorta and out to the body without going through the lungs. Soon after a baby is born, the ductus arteriosus should close up to prevent mixing oxygen-poor blood from the pulmonary artery with oxygen-rich blood from the aorta. If a doctor never detects the defect, the baby may grow into an adult with PDA, although this is rare.
Premature birth can put babies at risk. PDA is more common in girls than boys. In the rare case that PDA goes undetecte an adult with the defect may experience symptoms that include heart palpitations , shortness of breath , and complications such as high blood pressure in the lungs , an enlarged heart , or congestive heart failure.
A doctor will usually diagnose PDA after listening to your childs heart. A chest X-ray may also be necessary to see the condition of a babys heart and lungs. An echocardiogram is a test that uses sound waves to create a picture of the babys heart.
Its painless and allows the doctor to see the size of the heart. It also lets the doctor see if theres any abnormality in blood flow. Echocardiogram is the most common method to diagnose PDA. An EKG records the electrical activity of the heart and detects irregular heart rhythms.
In babies, this test can also identify an enlarged heart. In cases where the opening of the ductus arteriosus is very small, no treatment may be necessary. In this case, your doctor will want to monitor the PDA as the baby grows. The opening can close as an infant gets older. In a premature baby, a drug called indomethacin can help close the opening in PDA.
In older infants and children, further treatment may be necessary. However, younger infants can have this treatment if they have symptoms. If the opening is large or it doesnt seal on its own, surgery may be necessary to correct the defect. For surgical procedures, your doctor may prescribe antibiotics to prevent bacterial infection after leaving the hospital. In an infant or child with a small PDA, your doctor may recommend a trascatheter device closure procedure, according to the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
A catheter is a thin flexible tube that is guided through a blood vessel starting in the groin and is guided to your childs heart. A blocking device is passed through the catheter and placed in the PDA. The device blocks the blood flow through the vessel and allows normal blood flow to return. Its very unusual for PDA to go undetected into adulthood.
Most cases of PDA are diagnosed and treated soon after birth. The larger the opening is, the worse the complications. If it does, however, it can cause several health problems.
However rare, untreated adult PDA can lead to other medical conditions in adults , such as: In very serious cases of untreated adult PDA, extra blood flow can eventually increase the size of the heart, weakening the muscle and its ability to pump blood effectively. Recovery for premature babies will depend on how early the baby was born and whether or not other illnesses are present. Most infants will make a complete recovery without experiencing any PDA-related complications. Patients with a moderate- or large-sized patent ductus arteriosus may develop problems related to the increased blood flow to the lungs.
If the doctor suspects a heart defect, he or she might request one or more of the following tests: 1. PDA can cause a heart murmur that the doctor can hear through a stethoscope. Sound waves produce images of the heart that can help the doctor identify a PDA, see if the heart chambers are enlarge and judge how well the heart is pumping. Treatments for patent ductus arteriosus depend on the age of the person being treated. Options might include: 1. The doctor will monitor your baby’s heart to make sure the open blood vessel is closing properly. For full-term babies, children and adults who have small PDAs that aren’t causing other health problems, monitoring might be all that’s needed.
If you or your child has a congenital heart defect or has had surgery to correct one, you might have some concerns about aftercare. This test also helps t. Preventing infection. For most people who have a patent ductus arteriosus , regularly brushing and flossing teeth and regular dental checkups are the best ways to help prevent infection. People and parents of children who have congenital heart defects often worry about the risks of vigoro. In many cases, the diagnosis and treatment of a patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) is critical for survival in neonates with severe obstructive lesions to either the right or left side of the heart.
The patient presentation of patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) varies widely. Although frequently diagnosed in infants, the discovery of this condition may be delayed until childhood or even adulthood. In isolated patent ductus arteriosus (PDA), signs and symptoms are consistent with left-to-right shunting. The shunt volume is determined by the size of the open communication and the pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR). Galen initially described the ductus arteriosus in the early first century.
Harvey undertook further physiologic study in fetal circulation. Gross successfully ligated a patent ductus arteriosus (PDA) in a 7-year-old child. Pulmonary hypertension (PHTN) and other presentations such as heart failure and edema are the identified complications of longstanding PDA, but adult case with no permanent heart symptoms and PHTN was.
Laustela E, Tala P, Halttunen P. A report of operated cases). Closure of the calcified patent ductus. A new operative method utilizing cardiopulmonary bypass. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.
Whereas ≈ of the fetal cardiac output is from the right ventricle, only to passes through. The factors responsible for persistent. Whereas spontaneous closure of the ductus arteriosus (DA) is likely in term infants, it is less so in preterm ones.