What is the importance of a normative approach? What are some examples of normative ethics? Quick Reference A theoretical, prescriptive approach to sociological studies that has the aim of appraising or establishing the values and norms that best fit the overall needs and expectations of society. Normative generally means relating to an evaluative standard. Normativity is the phenomenon in human societies of designating some actions or outcomes as good or desirable or permissible and others as bad or undesirable or impermissible.
A norm in this normative sense means a standard for evaluating or making judgments about behavior or outcomes.

Closing the gap between rules (what is supposed to happen) and norms (what actually happens), eliminates confusion and. Using the group process as a means of. Behavioral decision research involves normative , descriptive , and prescriptive approaches. According to the normative approach to politics, political thought is based on certain ideals and philosophies.
In comparison to empirical political theory, which describes politics according to measurable hypotheses, the normative approach is more concerned with philosophical ideas than it is with scientifically studying behaviors. It includes the formulation of moral rules that have direct implications for what human actions, institutions, and ways of life should be like. Thus, it is an attempt to figure out what people shoulddo or whether their current moral behavior is reasonable.
Hypotheses or other statements about what is right and wrong, desirable or undesirable, just or unjust in society.

The majority of sociologists consider it illegitimate to move from explanation to evaluation. In their view, sociology should strive to be value-free, objective, or at least to avoid making explicit value-judgements. The term is commonly used in reference to the discussion of general theories about what one ought to do, a central part of Western ethics since ancient times.
This is a normative claim because it goes beyond simply observing that this action is treated as wrong in one place and treated as right in another. These theories are rooted in first principles thinking, or logic. Basically, it would be what a perfectly rational agent would do, assuming the world itself is also perfectly rational.
The most prominent of these is utility theory, founded on a set of intuitively appealing axioms. It describes options in terms of a set of attributes, or features, that an individual might like or dislike about them. In contrast, meta-ethics, as the term suggests, is a study of the nature of ethics. It is the branch of philosophical ethics that investigates the set of questions that arise when considering how one ought to act, morally speaking. As a result of this subjective approach has been introduced in accounting.
It has been believed by the accounting experts that the positive accounting theory that has been followed in for farming the accounting polices does not help in developing and improving the accounting practices. Keep scrolling for more. Definition of normative.
This information is useful for scientists, doctors and advertisers alike. To describe development it is necessary to focus both on typical patterns of change ( normative development) and individual variations in patterns of change (i.e. idiographic development). Although there are typical pathways of development that most people will follow, no two persons are exactly alike.
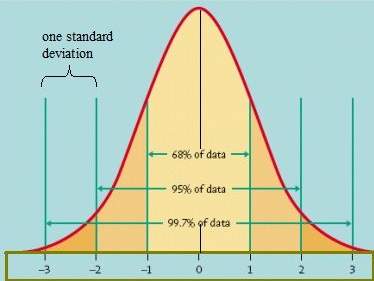
A perspective which assumes that all behavioral phenomenon exists according to the normal distribution curve thereby signifying that a majority population lies in the center while the rest of them occupy less portions in the either extreme ends.
Important normative theories Utilitarianism. Classical utilitarianismsays that the right actionis that which produces the greatest balance of overall. Kantian ethics stems from the work of the great Germanphilosopher Immanuel Kant.
Ethical intuitionism. Virtue ethics, advocated by Aristotle, focuses on the inherent character of a person rather than on specific actions. Instead of looking at what is already happening at companies today, normative accounting theory tells accounting. Scientists use the scientific method to gather this data and apply it to the generated hypothesis.
The central idea of the normative approach to the study of politics is politics or analysis of state or the functions of state are to be viewed in the light of what ought to be rather that what they are. The normativeness wants to give preference to should and ought to be.