Is a testamentary trust irrevocable? Can there be more than one testamentary trust? Will and probate before testamentary? A testamentary trust is created through a will. Non-testamentary trusts are called living trusts or inter vivos trusts.
Testamentary trusts become effective when the. These are trusts created. Usually this type of trust is made within a will often to create a trust for minors. When a trust is included in a will, the will goes into effect immediately, but the trust is not actually created until after the death of the will maker. See full list on nolo.
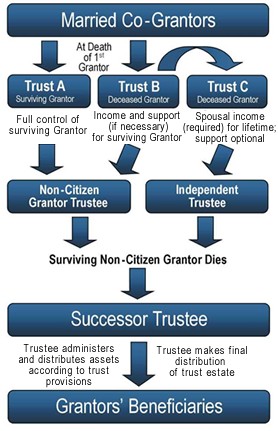
Non – testamentary trusts take effect when the grantor signs the trust , has it notarize and transfers property into the trust. This type of trust is called an inter vivos or living trust because it goes into effect during the grantors lifetime. Inter vivos trusts can be either revocable or irrevocable. In contrast to these types of trusts, a testamentary trust does not take effect until death of the trust maker, and at that time the trust becomes irrevocable. Because it does not take effect during the grantors lifetime, the grantor is free to make changes to the trust until his or her death.

Using testamentary trust in a will allows you to leave a gift to a child and also to name a trusted guardian as trustee of that gift. The trustee manages the trust until the minor becomes old enough to manage the property him or herself. The age at which the minor receives the property outright is determined by the trust maker and is stated in the trust. The primary purpose of most living trusts is to avoid probate. Unlike living trusts, testamentary trusts do not avoid probate.
The executor will probate the will and as part of the probate process, he or she will create the trust. It is frequently used when the beneficiary or beneficiaries are children or disabled people. The terms of the trust are specified in the will. Unlike a living trust , a testamentary trust comes into existence only after the settlor dies. Many wealthy testators maintain control over their property after death through testamentary trusts.

You can read a Clearlaw article on the testamentary trust structure generally and its benefits here. Then, the probate process will take place. While other types of trusts may avoid probate, a testamentary trust must go through the.
Your last will and testament can provide for more than one testamentary trust. Simple Paperless Solutions – Try Free! Real Estate, Family Law, Estate Planning, Business Forms and Power of Attorney Forms. A will may contain more than one testamentary trust , and may address all or any portion of the estate.
A trust can also be created after someone’s death, called a testamentary trust. Living trusts can be revocable, meaning you can cancel the trust and take your property back, or irrevocable, but both allow you to put property into the trust while you are alive. An example of a testamentary trust that is a revocable trust is a trust that can be revoked at any time.
The Revocable Living Trust. In the US, the revocable living trust is by far the most-popular form of trust used for estate planning purposes. It provides for the distribution of all or part of the estate. Because a testamentary trust is created upon death, the person cannot fund the testamentary trust during life.

On the other han an inter vivos trust is one that is created by someone during their life. So even though the testator creates the will while he is alive, the trust does. Each trust has different tax rules. At the bottom of this page you will find information on public trusts and public investment trusts and the different trust codes.
In either case, it is the trustee who is charged with administering the trust in strict accordance with its terms.