How to appeal NCAT decision? What does NCAT stand for? See full list on olg. NCAT deals with a broad and diverse range of cases. Select a case type to find out how NCAT can resolve your issue or dispute.
Housing and property.

Consumers and businesses. Administrative review and regulation. Professional discipline. If a person is not satisfied by the reviewable decision of an agency, they may apply to NCAT to review the decision. The Tribunal has the power to review administrative decisions made by NSW Government agencies.
This can include government agency decisions in respect of the use and access to personal information held by the government, firearms licences, guardianship management and administrative decisions made in respect of community services. The law relating to administrative decisions is quite complex. If you believe that you are entitled to a review of an administrative decision you should seek expert legal advice.
Once an application has been lodged with NCAT , a first hearing date is usually set within six weeks.

Before making an application to NCAT, a party to a home building disputemust first refer their matter to NSW Fair Trading. A letter or order from NSW Fair Trading is required to be attached to a NCAT application. The Tribunal can make a determination in respect of a home building dispute where the claim is no more than $50000. Disputes can include the construction of a new home, an extension to an existing home, bathroom or kitchen renovations and swimming pool installations. Disputes for determination can include an owner’s failure to pay or where building works have not been carried out as agreed including defective or incomplete work.
Disputes are commonly determined by NCAT in respect of unpaid rent, an increase of rent, bonds, termination of tenancy agreementsand repairs. NCAT can only determine matters where the amount in dispute is no more than $1000. That amount is increased to $30for disputes in relation to a rental bond. Either a tenant or a landlord can make an application to have their dispute determined by NCAT. Matters that relate to termination are first heard within three weeks from the date the application is lodged.
All other matters are first heard within four weeks. NCAT can determine disputes between a tenant and a landlord in respect of a retail lease. This can include, amongst other things, a dispute about payment of money, amendments to a lease, or a claim for repairs.
Before lodging an application with the Tribunal, parties to a retail lease must first attempt mediationwith the NSW Small Business Commissioner. If mediation is ultimately unsuccessful, the parties will receive a certificate from the Commissioner, which must be attached to a NCAT application. The retail lease dispute will be listed for a directions hearing within four weeks of the application being lodged. The NCAT website hosts all application forms in PDF.
Online lodgment is available for selected types of matters. Fees may apply when you file an application or use registry services.
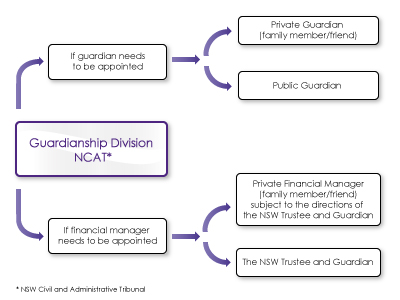
There are four divisions that can deal with your matter: 1. Guardianship Division 4. Occupational Division If you know which NCAT division applies to your matter, you can directly download the relevant application form on the NCAT website. Disputes determined by NCAT have strict limitation periods which must be adhered to. If you believe you have a dispute to be determined by the tribunal, you should seek legal advice promptly. LegalVision’s specialised litigation teamhave a wealth of experience in advising clients in relation to their NCAT disputes. North Carolina AT State University B. Supply of Goods and Services.
The tribunal’s job is to decide whether or not you have been unlawfully discriminated against, and if you have, what should be done about it. Home Building Disputes. The guideline also identifies alternative routes one might follow in various circumstances. NCAT can make binding decisions ordering the agency or organisation.
For example, it can order the agency or organisation to change their codes of practice, apologise, or take action to address any damage. When can compensation be ordered? Compensation can only be ordered in limited circumstances.
National Center for Asphalt Technology at Auburn University.