How dangerous is H pylori? Iatrogenic transmission of H. For the general population, the most likely mode of transmission is from person to person , by either the oral-oral route (through vomitus or possibly saliva) or perhaps the fecal-oral route. Helicobacter pylori) is passed from person to person by contaminated feces in food or water and poor hygiene practices. Learn about symptoms, treatment, and causes of H.

This usually happens during childhood. A common cause of peptic ulcers, H. If you develop signs and symptoms of a peptic ulcer, your doctor will probably test you for H. See full list on mayoclinic. When signs or symptoms do occur with H. An ache or burning pain in your abdomen 2. Living in crowded conditions.

Having a reliable supply of clean, running water helps reduce the risk of H. People living in developing countries, where crowded and. Complications associated with H. This can allow stomach acid to create an open sore (ulcer). About percent of people with H. Inflammation of the stomach lining. In areas of the world where H. Whether there is a benefit to treating H. Together you can decide whether you may benefit from H. Transfer of the bacterium remains an open topic, but it is likely that infection is usually acquired at a young age, particularly where lower socio-economic conditions prevail.
Transmission via an external source such as water supply is a possibility but, in general, infection is probably passed from person to person. Arguments for and against faecal-oral, oral-oral and gastric-oral transmission have been presente but the dominance of one of these routes is still to be determined. In northern California, 7household members were tested for H. The route of transmission of H pylori infection has been widely hypothesised but the exact mode(s) of transmission is still unknown.
Currently, several routes of transmission have been postulated including oral-oral, faecal-oral, iatrogenic, fomite, and vector borne, but no definite transmission pathway(s) has yet been identified.
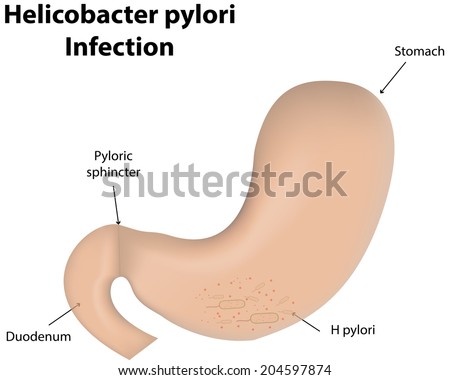
Thirteen years after the culture of H. Marshall and Warren, we still do not know its major mode of transmission. Childhood represents the major period of acquisition of infection in the third worl but infection is rare in children in the developed world. This bacterium causes gastritis and other common stomach diseases such as nausea, bloating, and heartburn. All of these can lead to the inflammation of the stomach. So, kissing and sharing utensils are two common ways the bacteria spreads.
H pylori penetrates the yeast and resides in a vacuole where it can survive heat (100°C for minutes), dehydration (37°C for months), and chlorination (ppm). This symbiotic relationship may prolong the viability of H pylori and play a crucial part in sexual transmission. You can also contract H. These data suggest that the case for faecal-oral transmission of H. A, is not proven and that other modes of transmission , for instance through oral-oral contact, should also be considered.
During a breath test, you swallow a pill, liquid or pudding that contains tagged carbon molecules. Your body absorbs the carbon and expels it when you exhale. The bacteria are believed to cause stomach problems when they penetrate the stomach’s mucous lining and generate.
It’s more common in countries or communities that lack clean water or good sewage systems. Hypothetically, the more the duration of breastfeeding lasts, the greater the baby exposes unhygienic conditions and becomes infected by H. There was an interesting determination from Gambia.