Instant Downloa Mail Paper Copy or Hard Copy Delivery, Start and Order Now! Is a Charitable Remainder Trust revocable? What is a charitable trust? Is a testamentary trust an irrevocable trust?
Are charitable trusts tax exempt? It is frequently used when the beneficiary or beneficiaries are children or disabled.

Further, proper use of a testamentary CLAT not only zeroes out the estate tax but also offers a donor the chance to leave a charitable legacy with the organization of his or her choosing. Also known as a will trust or a trust under will, a testamentary trust provides for the distribution of an estate into a trust when the person who created the trust dies. In this guide, we dive deeper into what exactly a testamentary trust is, how to create one and who can create one.
Although incorporating a testamentary CRT in an estate plan does not offer an income tax deduction an under current law, is not necessary to avoid income taxation of pre-death appreciation, it does offer significant benefits. See full list on pgdc. Because a CRT is a tax-exempt entity, generally it will be beneficial to have it, rather than the post-mortem administrative entity, receive the taxable income generated by the bequest to it during administration.
Achieving this goal, even in part, presents a number of challenges. Pending ultimate distribution, s. The post-mortem entity.

Section 641(b) taxes its income in the same manner as in the case of an individual, except as specifically otherwise provided. Thus, except to the extent its income is offset by an allowable deduction, the post-mortem entity itself is taxed on the income it earns each year. Assets used to fund an inter vivos CRT are specifically selected for that purpose.
Those available to fund a testamentary residuary CRT, on the other han may include assets that are not suitable for such purpose. Whenever the CRT is a residuary beneficiary, the assets comprising the residue must be scrutinized early in the administration of the post-mortem entity to identify those, if any, which should not be distributed to the CRT and to determine how to deal with them. As noted at the outset, unless the anticipated term of the trust is relatively short, the most important and attractive long-term feature of the CRT from the standpoint of its creator and income beneficiary may be its exemption from income tax.
That exemption is lost, however, in any taxable year in which it has any unrelated business taxable income within the meaning of IRC §51 determined as if the unrelated business income tax applied to a CRT. No UBTI received from ent. Interrelated computations of estate tax. If the charitable remainder trust has a taxable income beneficiary, i. Includible portion of inter vivos CRT includible in the taxable estate of the decedent.
Not all of the corpus may be includible, however, if the decedent is not deemed to have retained the right to the entire income from the corpus. Because of the tax-exempt status of the CRT, a major objective of post-mortem administration is to have income earned during administration taxed to the beneficiaries, including the CRT, rather than to the entity. A will may contain more than one testamentary trust , and may address all or any portion of the estate. By including a formula and specific wording, a testamentary trust can be structured so that, upon death of the Trust Creator, a charitable contribution is made to a public charity equal in size to the amount of estate taxes that would otherwise be owed to the government. A testamentary trust is a trust contained in a last will and testament.
It provides for the distribution of all or part of an estate and often proceeds from a life insurance policy held on the person establishing the trust. There may be more than one testamentary trust per will.
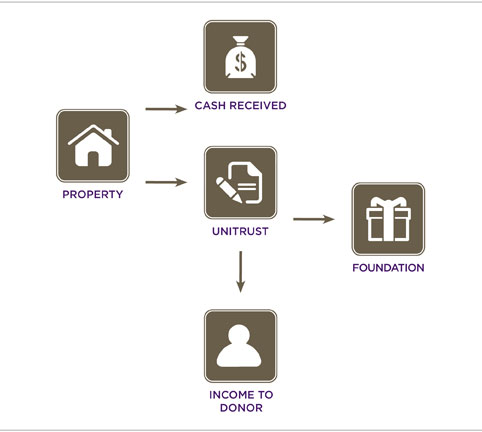
While these gift plans will not generate tax savings during your lifetime, they may reduce estate taxes and provide life income for a loved one. Item IV of the will, which established the trust,. Since minors may be too young to effectively manage substantial property immediately, a testamentary trust allows the settlor to leave a gift to a child and also to name a trusted guardian as the gift’s trustee. Different types of trusts include testamentary trusts, living trusts, AB trusts, and charitable trusts.
A Charitable Remainder Trust (“CRT”) can be established during the lifetime of the creator of the trust (the “Grantor”) or upon the death of the Grantor. Transfers to a CRT established during the lifetime of a Grantor will produce an income tax deduction for the Grantor. Although the will is written while the decedent is alive, the trust itself doesn’t come into existence until the will has been probated and the executor settles the estate. If a testamentary trust is created which fails to name a trustee, or the named trustee refuses to accept the position or predeceases the settlor and no alternate trustee is named in the will nor effective provision made for appointment of an alternate trustee, the court shall appoint a suitable person as trustee. Testamentary wills do not take effect until the death of the grantor.
Sample testamentary charitable remainder annuity trust (CRAT) for a term of years. This procedure contains a sample declaration of trust that meets the requirements under section 6of the Code and 1. Transfer of irrevocable remainder interest to charity.