The lowest energy unoccupied molecular orbital is 2pσ, so that is where the extra electron will be added. The electron configuration of the C− ion will be. Molecular Orbital Diagram for Carbon Dimer (C2).
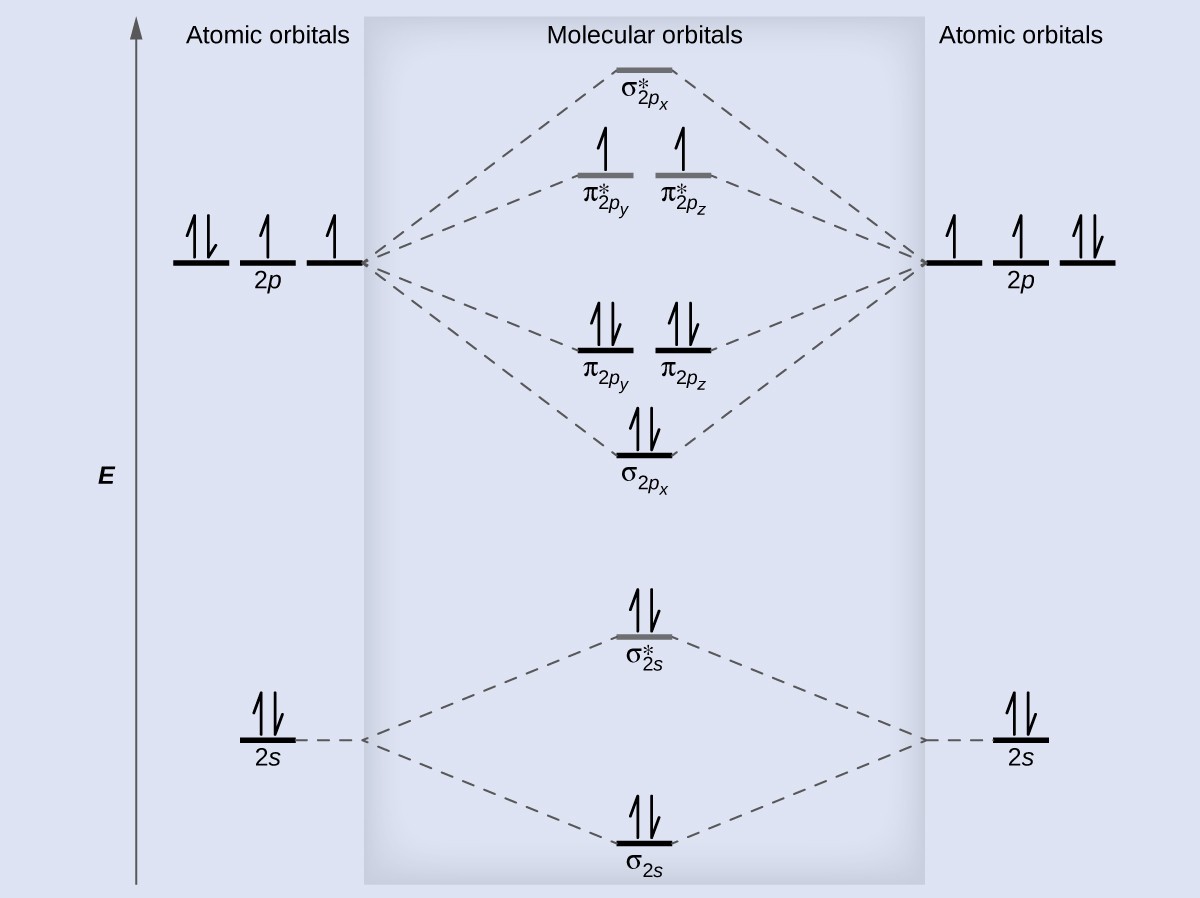
Fill from the bottom up, with electrons total. Bonding Order is and it is Diamagnetic. A molecular orbital diagram , or MO diagram , is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. How to do orbital diagrams?
What is molecular orbital model? If you see the MO diagram above, there are two unpaired electrons in the p-pi BO. This is what makes Cunstable. Atomic orbitals must have the proper symmetry and energy to interact and form molecular orbitals.
Photoelectron spectroscopy provides useful information on the energies of atomic orbitals. Next we’ll see that symmetry will help us treat larger molecules in the LCAO-MO theory framework. Learn to draw molecular orbital electron configuration energy diagrams. Answer to Construct the molecular orbital diagram for Heand then identify the bond order.
Bond order: Click within the blue boxe. Schematic picture of the molecular orbital diagram obtained from MO theory. In VB, the bond picture arises from considering that the C atom bears a sp hybridization. When we draw the CMO, we have everything up till the PiPy Orbitlal fille and the next orbital tht would be filled would be the sigma2Pz orbital.
In the diagram below, label each molecular orbital (MO) for C2. Question 1) By drawing molecular orbital diagrams for B C, N O and F predict which of these homonuclear diatomic molecules are magnetic. Question 2) Based on the molecular orbital diagram for NO, which of the following electronic configurations and statements are most correct? The linear combination of atomic orbitals always gives back the same number of molecular orbitals. When atomic orbitals add in phase, we get constructive interference and a lower energy orbital.
One of the molecular orbitals in this molecule is constructed by adding the mathematical functions for the two 1s atomic orbitals that come together to form this molecule. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals , because they do not contain the valence electrons.

Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals. The 2s orbitals will overlap to form 2sσ and 2sσ. Total number of electrons = 2×6-1=11. As for bond orders it is 12e in bonding orbitals e in antibonding orbitals. Diatomic Species Mo Theory Chemogenesis General notes on molecular orbital diagrams.
Interact and form molecular orbitals. Usually, the z-axis is the bond axis. The carbon atoms and orbitals are. Ethylene is the simplest molecule that has a double bond. As we saw from the valence bond model, we should find the presence of a σ-bond framework, and a. Each line in this diagram represents one pair of shared electrons.
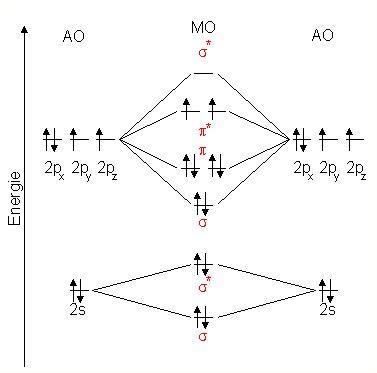
The combination of the 2s orbitals from the two atoms form a sigma bonding and sigma antibonding orbitals in a way very similar to the case of the hydrogen molecules, because the 2p orbitals have little to do with the 2s orbitals. For example, the XeFmolecule belongs to the D4h point group. XeFcontains one Crotation axis, one Crotation axis, and four Cperpendicular rotation axis, 2σv planes, 2σd planes and 1σh plane, those composed the character table of the D4h Point group.