Molecular Weight: 30. Structures Expand this section. Names and Identifiers Expand this section. Even rather simple molecular orbital (MO) theory can be used to predict which we start reading from the bottom of the diagram because this is how MO diagrams are constructe Diberyllium, Be has a bond order of zero and is unknown. From the electronic configuration it is clear that there is no singly filled atomic orbital present in beryllium.
Bonding Order is meaning it does not bon and it is diamagnetic. Now, talking about Be its electronic configuration is 1s²2s² and the MO diagram of Be(hypothetical) is shown below. Be molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both beryllium atoms.
The molecule is, in fact, present in appreciable concentration in lithium vapor at temperatures near the boiling point of the element. All of the other molecules in Table 8. These are inorganic compounds containing only metal atoms, with the largest atom being a alkaline earth metal atom. It has a linear structure.

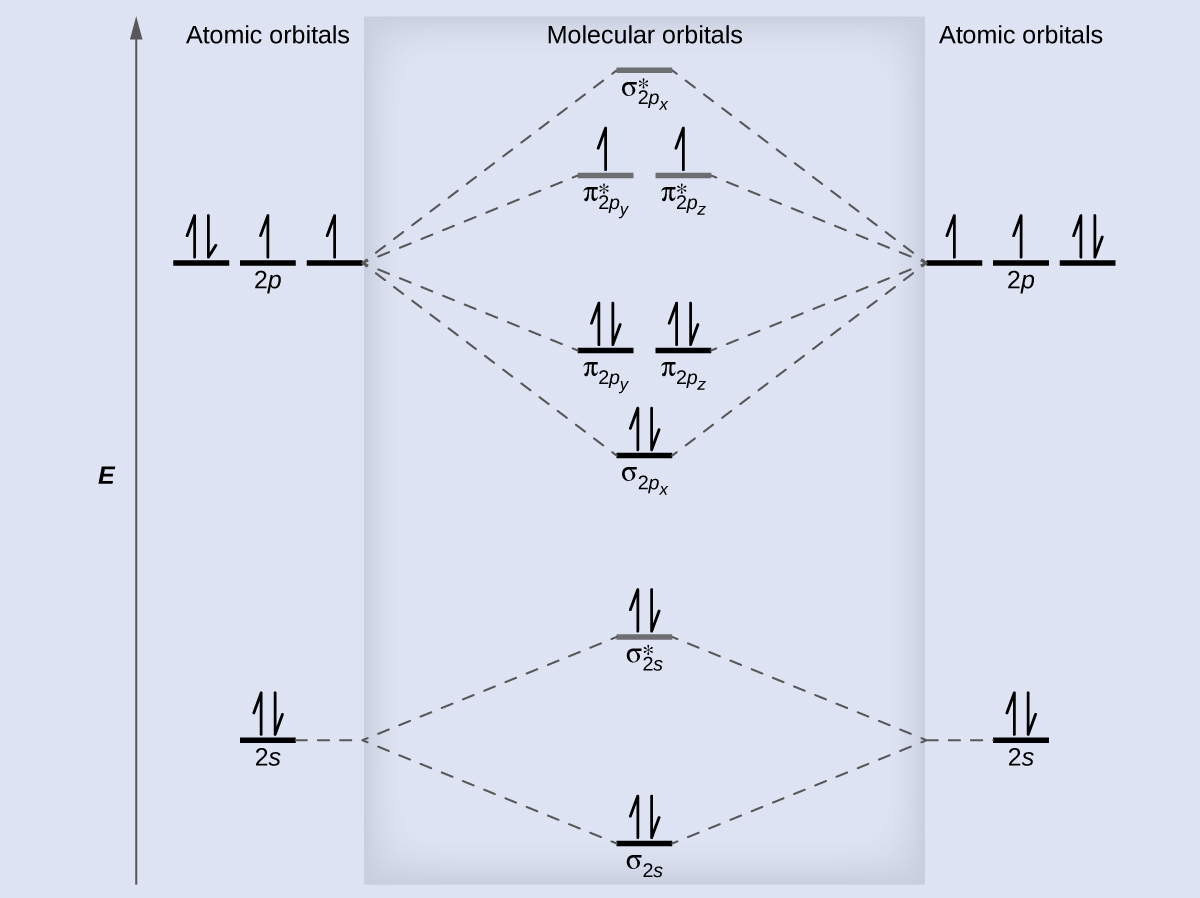
Dipole moments of each H–Be bond are equal and are in opposite directions. Then we rank them in order of increasing energy. We can ignore the 1s orbitals, because they do not contain the valence electrons. Each boron atom has one 2s and three 2p valence orbitals. The molecular orbitals are filled in the same manner as atomic orbitals, using the Aufbau principle and Hund’s rule.
Part of this theory is the concept of bond order which gauges whether a molecular bond would be stable or unstable. Bonding: Bonding is a term to describe when atoms donate or share. Step 2: Draw the molecular orbital diagram. The amount of protons and neutrons remains the same at 4. Therefore, Beryllium will have four protons, four neutrons, and two electrons.
Beryllium molecule is also not possible because according to valence bond theory the number of repulsive forces is more than the number of attractive forces. So Beis not possible. From the ground-state electron configurations of Liand Be, predict which molecule should have the greater dissociation energy. Bemolecule does not exist. We now know that there are two electrons in the antibonding orbitals and in the bonding orbitals.
I understand that Be cannot exist, since it has as many electrons in the antibonding as in the bonding orbitals. Using the molecular orbital energy ordering for second-period homonuclear diatomic molecules in which the p2p orbitals lie at lower energy than the s2p, draw MO energy diagrams and predict the bond order in a molecule or ion with each number of total valence electrons. Will the molecule or ion be diamagnetic or paramagnetic? A bond involving molecular orbitals that are symmetric with respect to rotation around the bond axis is called a sigma bond (σ-bond).

If the phase changes, the bond becomes a pi bond (π-bond). Paramagnetic materials, those with unpaired electrons, are attracted by magnetic fields whereas diamagnetic materials, those with no unpaired electrons, are weakly repelled by such fields. By constructing a molecular orbital picture for each of the following molecules, determine whether it is paramagnetic or diamagnetic. A molecular orbital diagram, or MO diagram, is a qualitative descriptive tool explaining chemical bonding in molecules in terms of molecular orbital theory in general and the linear combination of atomic orbitals (LCAO) method in particular. When comparing Beand H2: I. Beis more stable because it contains both bonding and antibonding valence electrons.
Hhas a higher bond order than Be2. His more stable because it only contains σ1s electrons. The Lewis structure for Beis nonexistent. A bond between two Be atoms will not form according to molecular orbital theory.
What is the formula of beryllium oxalate? We are showing below the molecular orbital diagram for Be2. Na and Nb are the number of electrons present in bonding and antibonding molecular orbitals respectively. Here we report the production of transgenic cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz) with starches containing up to amylose due to the constitutive expression of hair‐pin dsRNAs targeting the BEor BEgenes. Firstly, the use of molecular orbital diagrams allows you to predict the electronic configuration, if a molecule would exist or not (as you say, evaluating the bond order), and some magnetic properties.
Moreover, if you have the same molecule as O$_2$ and its ion O$_2^-$, etc, you can say the higher bond order, the bigger stability. In chemistry, a molecular orbital is a mathematical function describing the location and wave-like behavior of an electron in a molecule. This function can be used to calculate chemical and physical properties such as the probability of finding an electron in any specific region.
C₂ is the diatomic molecular species which has only π bonds according to molecular orbital theory. Electronic configuration of N₂ is 1s² 2s² and 2p³.