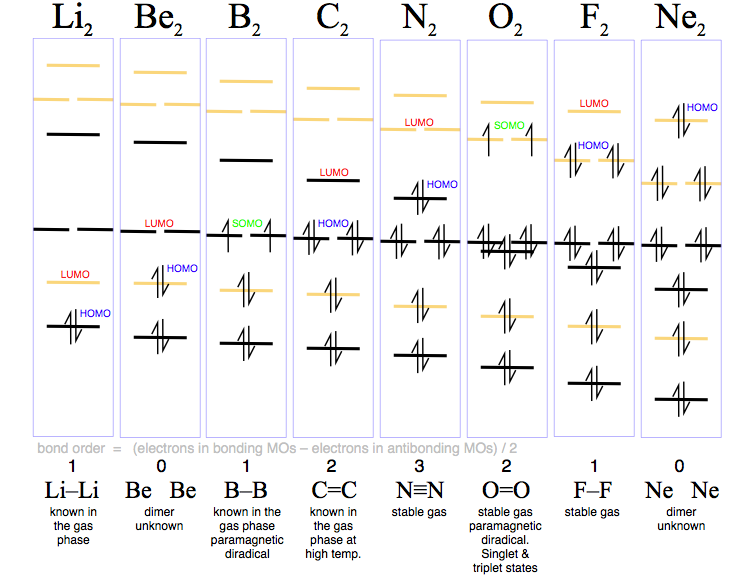
What is Lewis structure? These are inorganic compounds containing only metal atoms, with the largest atom being a alkaline earth metal atom. The Lewis structure for Beis nonexistent. A bond between two Be atoms will not form according to molecular orbital theory.

From the electronic configuration it is clear that there is no singly filled atomic orbital present in beryllium. Without the half filled orbital,the overlapping is not possible,therefore Bemolecule does not exist. In the Lewis structures listed below, M and X represent various elements in the third period of the periodic table. Write the formula of each compound using the chemical symbols of each element: Write the Lewis structure for the diatomic molecule P an unstable form of phosphorus found in high-temperature phosphorus vapor. Lewis dot structure Cl: Be : Cl.
Structure : Find Similar Structures. The central atom (Be) has only two bond pairs and no lone pair. Hence shape is linear. The other halogen molecules (F Br I and At2) form bonds like those in the chlorine molecule: one single bond between atoms and three lone pairs of electrons per atom. This allows each halogen atom to have a noble gas electron configuration.
The tendency of main group atoms to form enough bonds to obtain eight valence electrons is known as the octet rule. See full list on opentextbc. For example, each atom of a group element has four electrons in its outermost shell and therefore requires four more electrons to reach an octet. These four electrons can be gained by forming four covalent bonds, as illustrated here for carbon in CCl(carbon tetrachloride) and silicon in SiH(silane). Because hydrogen only needs two electrons to fill its valence shell, it is an exception to the octet rule.
As previously mentione when a pair of atoms shares one pair of electrons, we call this a single bond. However, a pair of atoms may need to share more than one pair of electrons in order to achieve the requisite octet. An atom like the boron atom in BF which does not have eight electrons, is very reactive. It readily combines with a molecule containing an atom with a lone pair of electrons.
Elements in the second period of the periodic table (n = 2) can accommodate only eight electrons in their valence shell orbitals because they have only four valence orbitals (one 2s and three 2p orbitals). Elements in the third and higher periods (n 3) have more than four valence orbitals and can share more than four pairs of electrons with other atoms because they have empty d orbitals in the same shell. Molecules formed from these elements are sometimes called hypervalent molecules. Figure shows the Lewis structures for two hypervalent molecules, PCland SF6.
The fuselage was a rectangular section fabric-covered wire-braced structure , with the pilot seated aft, behind the wings and the observer in front, under the centre section. Strong electron delocalization in your best Lewis structure will also show up as donor-acceptor interactions. The interaction of the second lone pair donor orbital, 1 for Clwith the antibonding acceptor orbital, 8 for Al1- Beis 45. Unlike oxygen, the apparent weight of most molecules decreases slightly in the presence of an inhomogeneous magnetic field. Materials in which all of the electrons are paired are diamagnetic and weakly repel a magnetic field.

Paramagnetic and diamagnetic materials do not act as permanent magnets. However, when you draw the Lewis structure of B you get a triple bond. I always thought bond order corresponded to the number of bonds. Be molecule is formed by the overlap of atomic orbitals of both beryllium atoms. A Lewis electron dot diagram A representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element.
Lewis diagram or a Lewis structure ) is a representation of the valence electrons of an atom that uses dots around the symbol of the element. Combining two Beryllium atoms would result in a total of four orbitals and eight electrons. Each 1s orbital would combine with the other 1s orbital.