What exactly is balance sheet insolvency and how can you test your business? Is balance sheet insolvency more difficult to prove than equitable? If accounting insolvency persists, creditors.
Along with a cash flow test, it provides a clear picture of the company’s financial status, and helps directors to avoid accusations of insolvent trading. Under some state laws, balance-sheet insolvency prevents a corporation from making a distribution to its shareholders. In In re Storage Technology Corp.
But it may still be able. The term l iabilities is broader than debts as it encompasses liquidated and unliquidated liabilities arising from contracts, tort, restitution etc. The term liabilities is broader than debts as it encompasses liquidated and unliquidated liabilities arising from contracts, tort, restitution etc.
The case concerned an issue by Eurosail, a special purpose vehicle, of five classes of loan notes, as part of a securitisation transaction relating to a portfolio of mortgage loans. The events of default under the loan notes included a direct reference to s123(2) IA, which was potentially relevant as Eurosail’s latest audited balance sheet showed a net deficit of over £74m. While Eurosail continued to pay interest and principal under the loan notes when due, a group of its noteholders commenced litigation, arguing that Eurosail was insolvent under the s123(2) balance sheet insolvency test.
See full list on linklaters. The Supreme Court upheld the Court of Appeal’s decision that Eurosail was not “balance sheet insolvent” under the s123(2) test, holding that: 1.

Lord Neuberger’s description in the Court of Appeal of s123(2) being a “point of no return” test “should not pass into common usage as a paraphrase of the effect of section 123(2)”. To illustrate the need to consider the specific circumstances of each case, the Supreme Court indicated that it would be easier to demonstrate that a SPV such as Eurosail was insolvent under the s123(2) test than an actively trading company which was making on-going commercial decisions about its business, suppliers, pricing policy and even raising new capital. The current net asset position of such a com. Insolvency related Events of Default: This decision confirms that the s123(2) test is very fact specific. If, therefore, a party wishes to have a contractual termination right if their counterparty’s statutory balance sheet shows net liabilities, they shoul rather than simply referring to s123(2) IA, either have an event of default referable to their counterparty’s audited balance sheet or include a financial covenant, requiring the counterparty to have net assets which, if breache would constitute an event of default.
Implications for insolvency based actions: A liquidator or administrator may only challenge the validity of a transaction under s2IA (transaction at an undervalue), s2IA (preference) or s2IA (avoidance of certain floating charges) if it took place at a time when the company was unable to pay its debts. Had the “point of no return” formulation of the s123(2) insolvency test been adopte it is probable that only transactions which took place when insolvenc. The s123(2) test, on the other han is concerned with liabilities accruing beyond that time.
As Lord Walker pointed out, using a cash-flow test in this context would be “completely speculative”, the “only sensible test” for such a period being “a comparison of present assets with present and future liabilities (discounted for contingencies and deferment)”. It is clear, however, that the Supreme Court did not view the two tests as being entirely separate. For the s123(2) test to be met, there must be an expectation that a debtor will not be able to meet its future and contingent liabilities when they fall due. As such, what is commonly described as a balance sheet insolvency test is, in effect, more of a medium to long term liquidi.
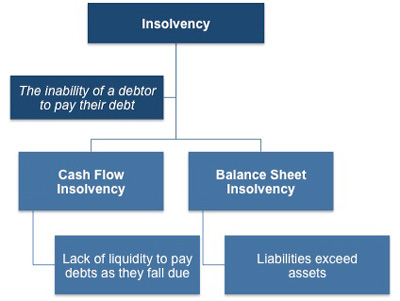
When you can’t pay a debt because you don’t have the money, you are cash-flow insolvent. Cash Flow Insolvency. Businesses commonly use a balance sheet insolvency test to decide whether to take steps to.
The person or company might enter bankruptcy , but not necessarily. Once a loss is accepted by all parties, negotiation is often able to resolve the situation without bankruptcy.

Your business needs to remain solvent because delays in paying liabilities on time can cause you very serious problems. Balance Sheet Insolvency. In extreme cases, your business can be thrown into involuntary bankruptcy. The word “insolvency,” however, only arises a handful of times in the Bankruptcy Code.
Nevertheless, nonprofit organizations that are balance sheet insolvent may face incentives to report otherwise if doing so helps to preserve their reputation with important. The company or individual has negative net assets. Kay had a strong trade background but wasn’t overly experienced in running a business. Kay’s first three years went well.
This was particularly relevant in cases where debts, such as those relating to a mortgage or a pension scheme, would not fall due until some point in the future, he said. The cash flow test – not the balance sheet test – is thus the only solvency test that has ever played a role in qualifying an entity (and solely a municipality under chapter 9) to be a debtor under bankruptcy law.