Meningococcal disease is caused by the bacterium. The guidance is based on the best scientific evidence available, from published and unpublished literature. It is now an online version ensuring that up to date information is accessible for all, in a format that is easy to navigate. A dose provided at ≥months (but before months) of age may be sufficiently immunogenic, especially in infants born to mothers with measles antibody derived from vaccination rather than natural infection. Administration in people with HIV The product information for Zostavax states that the safety and efficacy of Zostavax have not been established in adults with known HIV infection with or without evidence of immunosuppression.

This will ensure patients receive the best possible advice regarding vaccine preventable diseases. NHMRC for approval on updates to disease. Learn about immunisation Find out all about immunisation , how it protects you and your family and how to get started. Check the National Immunisation Schedule The National Immunisation Program (NIP) Schedule sets out free vaccinations for children, school programs, Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander peoples and other people at risk.
People over months of age with conditions that increase their risk of pneumococcal disease require a dose of 13vPCV at diagnosis followed by doses of 23vPPV. The strategy includes eight strategic priority areas for action to complement and strengthen the NIP. It’s an authoritative source used in everyday work by nurses, GPs and many other health professionals all over the country. No individual should be denied vaccination without serious consideration of the consequences, both for the individual and for the community.

Generally, a natural immunity exemption will only be applied to a specific antigen (not the whole schedule). The first symptoms of anaphylaxis may occur minutes or longer after vaccination. Coverage, Evaluation and Surveillance. Education and Training. Paediatric Enhance Disease Surveillance (PAEDS) Regional and global collaborations.
Research to Inform Policy. Many immunisation fact sheets, including translations, are only available as electronic versions for download and print. Australian Immunisation Handbook.
Before sharing sensitive information online, make sure you’re on a. Many of these vaccines are funded under the NIP, others are funded by state or territory government programs, and others are recommended but not currently funded under any program. The number of doses of Pneumovax is now limited to two lifetime doses. Management of patients. Patients who are suspected of having an AEFI may require further assessment before receiving further doses.
They can be referred to a specialist immunisation clinic or an immunologist for evaluation. These guidelines are based on the best scientific evidence available at the time of publication, from published and unpublished literature. All providers delivering immunisation services must report doses administered to the AIR. To apply to register with AIR, see Immunisation records and registers. This Operational Directive should be read in conjunction with these documents.
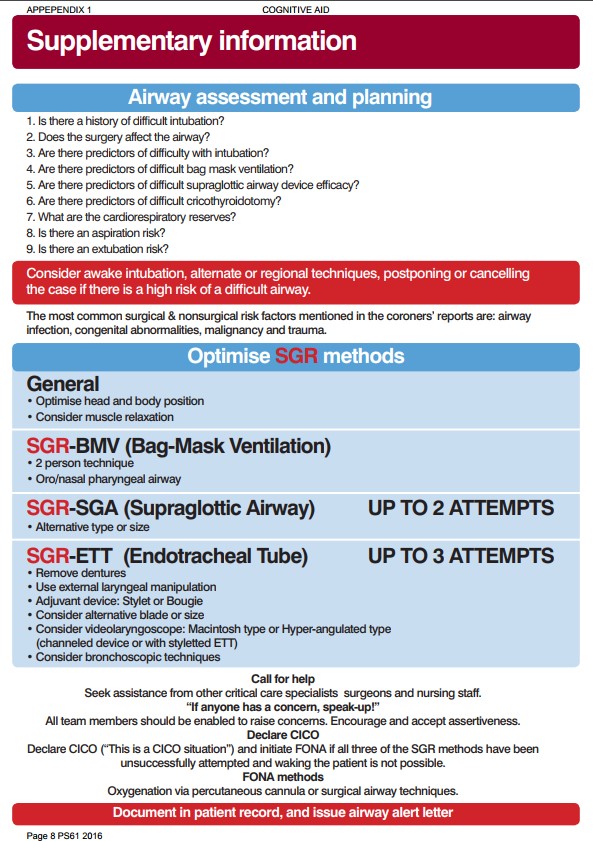
Immunisation is a successful and cost-effective intervention for prevention of disease. Get this from a library! Various placements may have different immunisation requirements. Department of Health and Ageing. Ensure that you are aware of what is required for your specific placement and refer to the handbo ok for more information about what each immunisation is for.
A major aim is to encourage practitioners to maintain the highest standard in the provision of age-appropriate immunisation services. Vaccines are rigorously tested on thousands of people in progressively larger clinical trials which are monitored for safety. Specified medical risk conditions – refer to online edition of AIH for additional doses and eligibility. Pneumococcal – people months of age with conditions which increase their risk of pneumococcal require a dose of 13vPCV at diagnosis followed by doses of 23vPPV.

Prevenar (Pneumococcal).