Identify Ultimate Ownership of Millions of Businesses and Commercial Entities Worldwide. All-in-One Due Diligence Solution. Which form of business ownership is the most common? What are the four basic patterns of business ownership?
A sole proprietorship is the most basic form of business ownership , where there is one sole owner who is responsible for the business.

It is not a legal entity that separates the owner from the business , meaning that the owner is responsible for all of the debts and obligations of the business on a personal level. In exchange for that liability, the owner keeps all the profits gained from the business. This form of business ownership is easy and inexpensive to create and has few government regulations, making it a more flexible type of ownership with complete control at the discretion of the owner. In addition, profits are taxed once, and there are some tax breaks available if the business is struggling.
See full list on education. Partnerships are a form of business ownership where two or more people act as co-owners. For a limited partnership, at least one of the partners has a limited liability, meaning they are not personally responsible for the debts of the business.
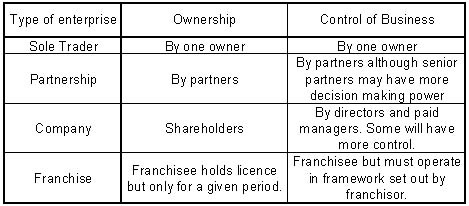
Regardless of the type of partnership, they are relatively easy and cheap to create, have few government regulations and are only taxed once, like a sole proprietorship. The added benefit of a partnership is the combination of knowledge and resources that are brought to the table thanks to the additional owners. Profits do have to be shared between owners and there is always the potential for conflicts to arise between partners over business decisions. Unlike the previous two examples, Corporations are a form of ownership that is a legal entity separate from its owners.
This creates a limited liability for all owners, but in a double taxation on profits (first as a corporate income tax, then as a personal income tax when the owners take their profits). Corporations tend to have an easier time raising capital then sole proprietors or partners in large part due to the greater sources of funding made available to them, such as selling stock. However, this does result in greater government regulations for corporations, such as requirements for more extensive record keeping. In addition, setting up a corporation is much more difficult, requiring more resources and capital to cover expenses and create legal documentation. This ownership form is best suited for fast growing or mature organizations that have owners looking for limited liability.
A form of business ownership that is taxed like a partnership but enjoys the benefits of a limited liability like a corporation is a “limited liability company”. In comparison to a corporation, it is simpler to organize and does not receive double taxation. While simultaneously receiving more credibility then a partnership or sole proprietor when it comes to gathering resources such as working capital. Unfortunately, this form of ownership is usually reserved for a group of professionals such as accountants, doctors and lawyers.
A lesser known ownership style, an S corporation is a type of business ownership that allows its owners to avoid double taxation because the organization is not required to pay corporate taxes. Instea all profits or losses are passed on to owners of the organization to report on their personal income tax.

This form of ownership does allow for limited liability, similar to a corporation, but without the double taxation. The disadvantages of this organization’s special nature is the increased level of government regulations and the restrictions on the number and type of shareholders it may have. This type of ownership is used in the mature stage of a businesses lifecycle and often by private organizations due to the restrictions on ownership. Franchising is a form of ownership far different from the ones previously mentioned.
It comes with a list of advantages including: training on how to operate your franchise, systems and technologies for day-to-day operations, guidance on marketing, advertising and other business needs, and a network of franchise owners to share experiences with. The main disadvantages to this ownership structure are franchising fees, royalties on sales or profits, and tight restrictions to maintain ownership. Franchise owners also have limited control over their suppliers they can purchase from, are forced to contribute to a marketing fund they have little control over. If a franchisee wants to sell their business, the franchisor must approve the new buyer. Despite these disadvantages, franchises are great for owners who are looking for an ‘out of the box’ to owning their own business.
It also offers limited liability to its owners and equal profit distribution based on ownership percentage. Disappointingly, the democratic approach to decision making in a longer decision making process as participation from all association members is required. Conflicts between members can also arise that can have a big impact on the efficiency of the business. Co-operatives are often used when individuals or businesses decide to pool resources to achieve a common goal or satisfy a common nee such as employment needs or a delivery service. The pros and cons of different business types of ownership , including sole proprietorship, partnering, corporations, and limited liability companies.
There are basically three types or forms of business ownership structures for new small businesses: 1. Forms of business ownership. Owners can opt to run their businesses as sole traders, partnerships or private limited companies. As the business expands it may decide to become a public limited.
ADVERTISEMENTS: The different types of business ownership are:- 1. Single Ownership (Private Undertaking). Joint Stock Company 4. When you start a business , you must decide whether it will be a sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation, or limited liability company (LLC). Cooperative Organisation (Or Societies) 5. These are the basic forms of business ownership : 1. It is easy to set-up and is the least costly among all forms of ownership. When starting a business , owners must decide what form of business entity to establish.
The type of business structure determines which income tax return form you file, and may impact how you structure health benefits for yourself (the owner ), your family, and your employees. Each business structure has distinct advantages and disadvantages compared to the other forms of ownership. Discuss these options with financial, tax and business advisors to determine which form of business ownership best fits your needs. Sole Proprietorships. This business formation is the most common among business owners in the United States.
Start studying types of business ownership. Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study tools. The business structure you choose influences everything from day-to-day operations, to taxes, to how much of your personal assets are at risk.
You should choose a business structure that gives you the right balance of legal protections and benefits.