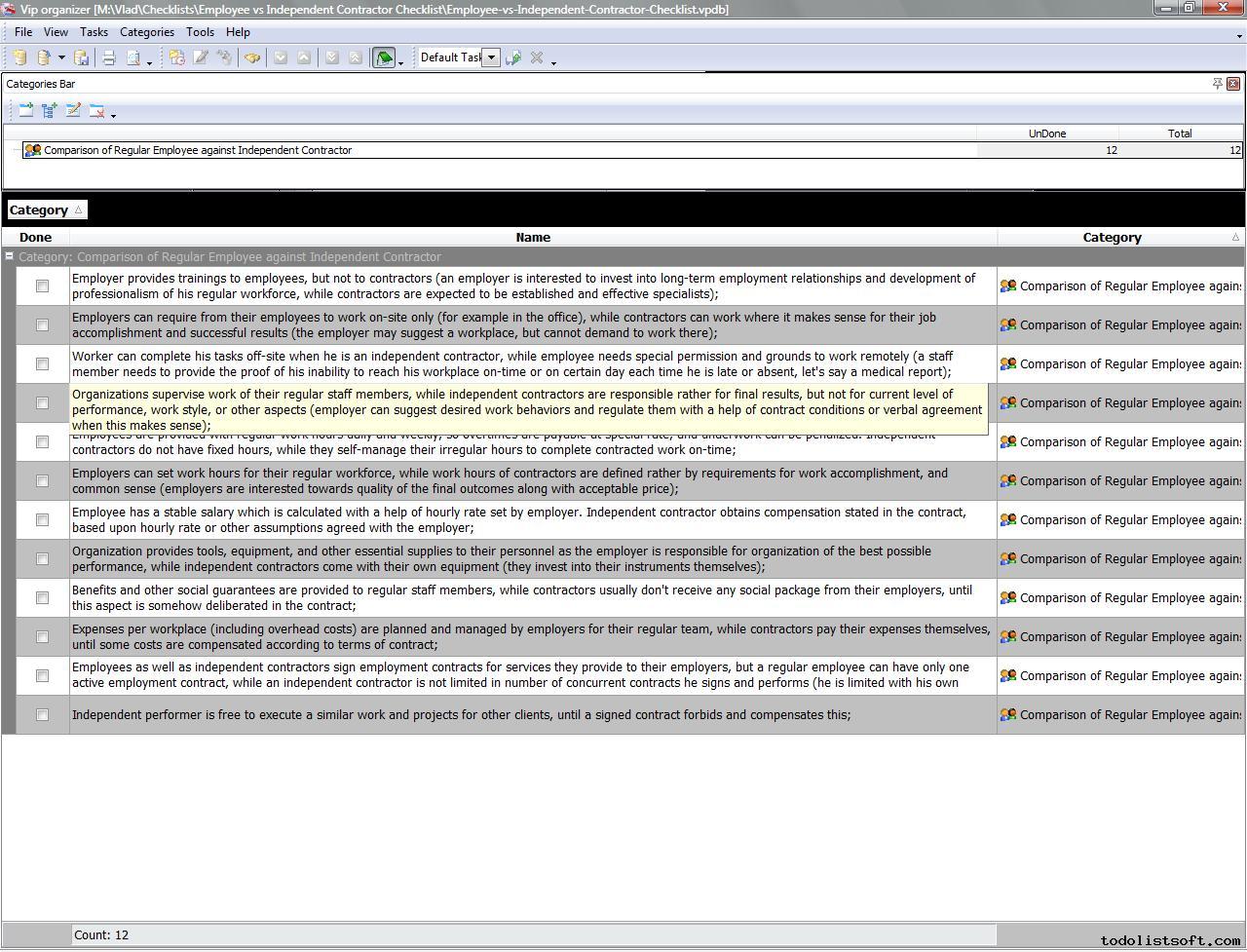
While it is easy to say that independent contractors are simply the opposite of full-time employees , it would serve us well to review in what distinct ways they differ. Whereas an employee is subject to the full authority and control of their employer , independent contractors work with multiple clients on a per project basis OR with one company for a specified period of time. Independent contractors are generally free to seek out business opportunities. An employee is generally guaranteed a regular wage amount for an hourly, weekly, or other period of time even when supplemented by a commission.
However, independent contractors are most often paid for the job by a flat fee. See full list on irs. Facts that provide evidence of the degree of control and independence fall into three categories: 1. Financial: Are the business aspects of the worker’s job controlled by the payer?
Type of Relationship: Are there written contracts or employee type benefits (i.e. pension plan, insurance, vacation pay, etc.)? Will the relationship continue and is the work performed a key aspect of the business? Some factors may indicate that the worker is an employee, while other factors indicate that the worker is an independent contractor.

There is no “magic” or set number of factors that “makes” the worker an employee or an independent cont. The form may be filed by either the business or the worker. The IRS will review the facts and circumstances and officially determine the worker’s status.
Be aware that it can take at least six months to get a determination, but a business that continually hires the same types of workers to perform particular services may want to consider filing the Form SS-8(PDF). Once a determination is made (whether by the business or by the IRS), the next step is filing the appropriate forms and paying the associated taxes. Forms and associated taxes for independent contractors 2. There are specific employment tax guidelines that must be followed for certain industries.
If you classify an employee as an independent contractor and you have no reasonable basis for doing so, you may be held liable for employment taxes for that worker (the relief provisions, discussed below, will not apply). Employment Tax Guidelines: Classifying Certain Van Operators in the Moving Industry(PDF) 2. If you have a reasonable basis for not treating a worker as an employee , you may be relieved from having to pay employment taxes for that worker. To get this relief, you must file all required federal information returns on a basis consistent with your treatment of the worker.
Employee or independent contractor checklist. Do you need an employee or independent contractor ? Use this accessible checklist template to find out, or to determine whether current workers are properly classified. How to tell a contractor from an employee? What is the difference between contractor and employee?
Is a contractor considered an at will employee? Should you hire employees or contractors? Routines and schedules established by the business for a worker suggest the worker is an employee.
Does the business provide training to the worker? An employee may quit at any time while an independent contractor may be liable for failure to complete a contract. Working with multiple clients generally indicates independent contractor status.
What all these factors try to determine is whether or not an employer has the right to control what a worker does and how and when he or she does it, as well as how much financial risk the worker has taken on for themselves or how much they have invested in their own business. The more control a business has over a worker, the more likely they should be classified as an employee. The more financial risk the worker has in terms of business profit and loss, or the greater their own investment in tools, equipment and facilities, the more likely they are to be classified as an independent contractor.
If a person falls into the employee status on more than 8-of the IRSguidelines, you should probably play it safe and classify them as an employee. The hiring entity must establish that the worker is free of such control to satisfy part A of the ABC test. A worker who is subject, either as a matter of contractual right or in actual practice, to the type and degree of.

Depending on the nature of the work and overall arrangement. If you hire a worker you must check if they are an employee or contractor. If you previously hired a worker without checking, review your decision now to make sure you got it right.
It is crucial for employers to understand the distinction between the two aforementioned types of workers, considering the serious penalties that. Businesses specify these categories in the IRS Form SS-8. Subcontractor: IRS Guidelines. The IRS has developed a list of factors it uses to determine employee or subcontractor status.
The IRS guidelines fall into three main categories: Behavioral Control Financial Control Relationship of the Worker and Firm. This applies even if the work is being done on a one-time basis. This worker is a temporary employee , not an independent contractor.